前言
实时数仓,难免会遇到join维表的业务。现总结几种方案,供各位看官选择:
查找关联(同步,异步) 状态编程,预加载数据到状态中,按需取 冷热数据 广播维表 Temporal Table Join Lookup Table Join
其中中间留下两个问题,供大家思考,可留言一起讨论?
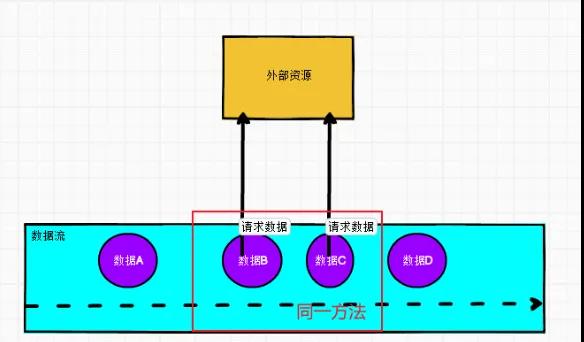
查找关联
查找关联就是在主流数据中直接访问外部数据(mysql,redis,impala ...)去根据主键或者某种关键条件去关联取值。
适合: 维表数据量大,但是主数据不大的业务实时计算。
缺点:数据量大的时候,会给外部数据源库带来很大的压力,因为某条数据都需要关联。
同步
访问数据库是同步调用,导致 subtak 线程会被阻塞,影响吞吐量

import com.alibaba.fastjson.{JSON, JSONArray, JSONObject} import com.wang.stream.env.{FlinkStreamEnv, KafkaSourceEnv} import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FlatMapFunction import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.SimpleStringSchema import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._ import org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.kafka.FlinkKafkaProducer import org.apache.flink.util.Collector def analyses(): Unit ={ val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = FlinkStreamEnv.get() KafkaSourceEnv.getKafkaSourceStream(env,List(\"test\")) .map(JSON.parseObject(_)) .filter(_!=null) .flatMap( new FlatMapFunction[JSONObject,String] { override def flatMap(jSONObject: JSONObject, collector: Collector[String]): Unit = { // 如果topic就一张表,不用区分,如果多张表,可以通过database 与 table 区分,放到下一步去处理 // 表的名字 val databaseName:String = jSONObject.getString(\"database\") // 表的名字 val tableName:String = jSONObject.getString(\"table\") // 数据操作类型 INSERT UPDATE DELETE val operationType:String = jSONObject.getString(\"type\") // 主体数据 val tableData: JSONArray = jSONObject.getJSONArray(\"data\") // old ֵ val old: JSONArray = jSONObject.getJSONArray(\"old\") // canal json 可能存在批处理出现data数据多条 for (i AsyncIO 可以并发地处理多个请求,很大程度上减少了对 subtask 线程的阻塞。
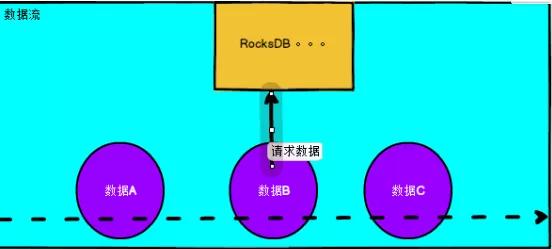
def analyses(): Unit ={ val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = FlinkStreamEnv.get() val source: DataStream[String] = KafkaSourceEnv.getKafkaSourceStream(env, List(\"test\")) .map(JSON.parseObject(_)) .filter(_ != null) .flatMap( new FlatMapFunction[JSONObject, String] { override def flatMap(jSONObject: JSONObject, collector: Collector[String]): Unit = { // 如果topic就一张表,不用区分,如果多张表,可以通过database 与 table 区分,放到下一步去处理 // 表的名字 val databaseName: String = jSONObject.getString(\"database\") // 表的名字 val tableName: String = jSONObject.getString(\"table\") // 数据操作类型 INSERT UPDATE DELETE val operationType: String = jSONObject.getString(\"type\") // 主体数据 val tableData: JSONArray = jSONObject.getJSONArray(\"data\") // old ֵ val old: JSONArray = jSONObject.getJSONArray(\"old\") // canal json 可能存在批处理出现data数据多条 for (i 首先把维表数据初始化到state中,设置好更新时间,定时去把维表。
优点:flink 自己维护状态数据,\"荣辱与共\",不需要频繁链接外部数据源,达到解耦。
缺点:不适合大的维表和变化大的维表。
.keyBy(_._1) .process( new KeyedProcessFunction[String,(String,String,String,String,String), String]{ private var mapState:MapState[String,Map[String,String]] = _ private var first: Boolean = true override def open(parameters: Configuration): Unit = { val config: StateTtlConfig = StateTtlConfig .newBuilder(org.apache.flink.api.common.time.Time.minutes(5)) .setUpdateType(StateTtlConfig.UpdateType.OnReadAndWrite) .setStateVisibility(StateTtlConfig.StateVisibility.NeverReturnExpired) .build() val join = new MapStateDescriptor[String,Map[String,String]](\"join\",classOf[String],classOf[Map[String,String]]) join.enableTimeToLive(config) mapState = getRuntimeContext.getMapState(join) } override def processElement( in: (String, String, String, String, String), context: KeyedProcessFunction[String, (String, String, String, String, String),String]#Context, collector: Collector[String]): Unit = { // 加载维表 if(first){ first = false val time: Long = System.currentTimeMillis() getSmallDimTableInfo() // 设置好更新时间,定时去把维表 context.timerService().registerProcessingTimeTimer(time + 86400000) } // 数据处理,过来一条条数据,然后按照自己的业务逻辑去取维表的数据即可 // 然后封装 放到collect中 collector.collect(null) } override def onTimer( timestamp: Long, ctx: KeyedProcessFunction[String, (String, String, String, String, String),String]#OnTimerContext, out: Collector[String]): Unit = { println(\"触发器执行\") mapState.clear() getSmallDimTableInfo() println(mapState) ctx.timerService().registerProcessingTimeTimer(timestamp + 86400000) } def getSmallDimTableInfo(): Unit ={ // 加载 字典数据 val select_dictionary=\"select dic_code,pre_dictionary_id,dic_name from xxxx\" val dictionary: util.List[util.Map[String, AnyRef]] = MysqlUtil.executeQuery(select_dictionary, null) dictionary.foreach(item=>{ mapState.put(\"dic_dictionary_\"+item.get(\"pre_dictionary_id\").toString,item) }) } } ) .filter(_!=null) .addSink( new FlinkKafkaProducer[String]( \"\", \"\", new SimpleStringSchema() ) ) v.execute(\"\")
思考下:直接定义一个Map集合这样的优缺点是什么?可以留言说出自己的看法?
冷热数据
思想:先去状态去取,如果没有,去外部查询,同时去存到状态里面。StateTtlConfig 的过期时间可以设置短点。
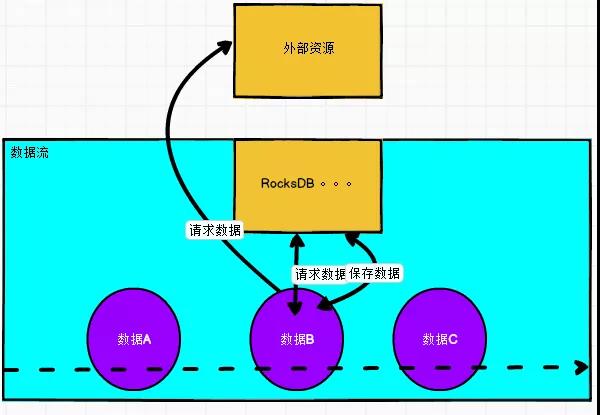
优点:中庸取值方案,热备常用数据到内存,也避免了数据join相对过多外部数据源。
缺点:也不能一劳永逸解决某些问题,热备数据过多,或者冷数据过大,都会对state 或者 外部数据库造成压力。
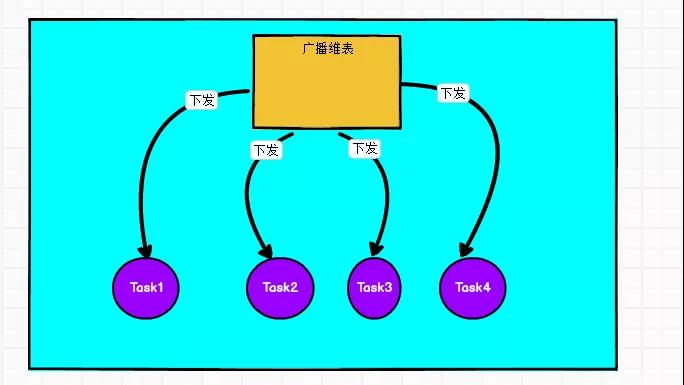
.filter(_._1 != null) .keyBy(_._1) .process( new KeyedProcessFunction[String,(String,String,String,String,String), String]{ private var mapState:MapState[String,Map[String,String]] = _ private var first: Boolean = true override def open(parameters: Configuration): Unit = { val config: StateTtlConfig = StateTtlConfig .newBuilder(org.apache.flink.api.common.time.Time.days(1)) .setUpdateType(StateTtlConfig.UpdateType.OnReadAndWrite) .setStateVisibility(StateTtlConfig.StateVisibility.NeverReturnExpired) .build() val join = new MapStateDescriptor[String,Map[String,String]](\"join\",classOf[String],classOf[Map[String,String]]) join.enableTimeToLive(config) mapState = getRuntimeContext.getMapState(join) } override def processElement( in: (String, String, String, String, String), context: KeyedProcessFunction[String, (String, String, String, String, String),String]#Context, collector: Collector[String]): Unit = { // 数据处理,过来一条条数据,然后按照自己的业务逻辑先去mapState去找,如果没有再去 外部去找 if (mapState.contains(\"xx_id\")){ // 如果存在就取 }else{ // 如果不存在去外部拿,然后放到mapState中 val dim_sql=\"select dic_code,pre_dictionary_id,dic_name from xxxx where id=xx_id\" val dim: util.List[util.Map[String, AnyRef]] = MysqlUtil.executeQuery(dim_sql, null) mapState.put(\"xx_id\",null) } // 然后封装 放到collect中 collector.collect(null) } } ) 广播维表
比如上面提到的字典表,每一个Task都需要这份数据,那么需要join这份数据的时候就可以使用广播维表。
val dimStream=env.addSource(MysqlSource) // 广播状态 val broadcastStateDesc=new MapStateDescriptor[String,String](\"broadcaststate\", BasicTypeInfo.STRING_TYPE_INFO, new MapTypeInfo<>(Long.class, Dim.class)) // 广播流 val broadStream=dimStream.broadcast() // 主数据流 val mainConsumer = new FlinkKafkaConsumer[String](\"topic\", new SimpleStringSchema(), kafkaConfig) val mainStream=env.addSource(mainConsumer) // 广播状态与维度表关联 val connectedStream=mainStream.connect(broadStream).map(..User(id,name)).key(_.1) connectedStream.process(new KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction[String,User,Map[Long,Dim],String] { override def processElement(value: User, ctx: KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction[String,User,Map[Long,Dim],String]#ReadOnlyContext, out: Collector[String]): Unit = { // 取到数据就可以愉快的玩耍了 val state=ctx.getBroadcastState(broadcastStateDesc) xxxxxx } }
「思考:」 如果把维表流也通过实时监控binlog到kafka,当维度数据发生变化时,更新放到状态中,这种方式,是不是更具有时效性呢?
(1)通过canal把变更binlog方式发送到kafka中。
(2)数据流定义成为广播流,广播到数据到主数据流中。
(3)定义一个广播状态存储数据,在主数据进行查找匹配,符合要求则join成功。
Temporal Table Join(FlinkSQL与Flink Table API)
由于维表是一张不断变化的表(静态表只是动态表的一种特例)。那如何 JOIN 一张不断变化的表呢?如果用传统的 JOIN 语法来表达维表 JOIN,是不完整的。因为维表是一直在更新变化的,如果用这个语法那么关联上的是哪个时刻的维表呢?我们是不知道的,结果是不确定的。所以 Flink SQL 的维表 JOIN 语法引入了Temporal Table 的标准语法,用来声明关联的是维表哪个时刻的快照。
普通关联会一直保留关联双侧的数据,数据也就会一直膨胀,直到撑爆内存导致任务失败,Temporal Join则可以定期清理过期数据,在合理的内存配置下即可避免内存溢出。
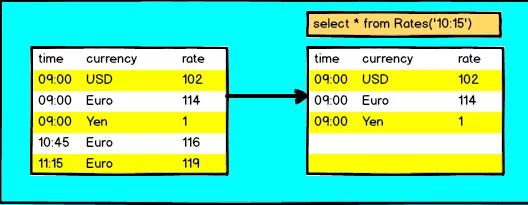
Event Time Temporal Join
语法
SELECT [column_list] FROM table1 [AS ] [LEFT] JOIN table2 FOR SYSTEM_TIME AS OF table1.{ proctime | rowtime } [AS ] ON table1.column-name1 = table2.column-name1
使用事件时间属性(即行时间属性),可以检索过去某个时间点的键值。这允许在一个共同的时间点连接两个表。
举例
假设我们有一个订单表,每个订单都有不同货币的价格。为了将此表正确地规范化为单一货币,每个订单都需要与下订单时的适当货币兑换率相结合。
CREATE TABLE orders ( order_id STRING, price DECIMAL(32,2), currency STRING, order_time TIMESTAMP(3), WATERMARK FOR order_time AS order_time ) WITH (/* ... */); CREATE TABLE currency_rates ( currency STRING, conversion_rate DECIMAL(32, 2), update_time TIMESTAMP(3) METADATA FROM `values.source.timestamp` VIRTUAL WATERMARK FOR update_time AS update_time, PRIMARY KEY(currency) NOT ENFORCED ) WITH ( \'connector\' = \'upsert-kafka\', /* ... */ ); event-time temporal join需要temporal join条件的等价条件中包含的主键 SELECT order_id, price, currency, conversion_rate, order_time, FROM orders LEFT JOIN currency_rates FOR SYSTEM TIME AS OF orders.order_time ON orders.currency = currency_rates.currency Processing Time Temporal Join
处理时间时态表连接使用处理时间属性将行与外部版本表中键的最新版本相关联。
根据定义,使用processing-time属性,连接将始终返回给定键的最新值。可以将查找表看作是一个简单的HashMap,它存储来自构建端的所有记录。这种连接的强大之处在于,当在Flink中无法将表具体化为动态表时,它允许Flink直接针对外部系统工作。
使用FOR SYSTEM_TIME AS OF table1.proctime表示当左边表的记录与右边的维表join时,只匹配当前处理时间维表所对应的的快照数据。
Lookup Table Join
Lookup Join 通常用于通过连接外部表(维度表)补充信息,要求一个表具有处理时间属性,另一个表使 Lookup Source Connector。
JDBC 连接器可以用在时态表关联中作为一个可 lookup 的 source (又称为维表)。用到的语法是 Temporal Joins 的语法。
s\"\"\" |CREATE TABLE users( |id int, |name string, |PRIMARY KEY (id) NOT ENFORCED |) |WITH ( |\'connector\' = \'jdbc\', |\'url\' = \'xxxx\', |\'driver\'=\'$DRIVER_CLASS_NAME\', |\'table-name\'=\'$tableName\', |\'lookup.cache.max-rows\'=\'100\', |\'lookup.cache.ttl\'=\'30s\' |) |\"\"\".stripMargin s\"\"\" |CREATE TABLE car( |`id` bigint , |`user_id` bigint, |`proctime` as PROCTIME() |) |WITH ( | \'connector\' = \'kafka\', | \'topic\' = \'$topic\', | \'scan.startup.mode\' = \'latest-offset\', | \'properties.bootstrap.servers\' = \'$KAFKA_SERVICE\', | \'properties.group.id\' = \'indicator\', | \'format\' = \'canal-json\' |) |\"\"\".stripMargin SELECT mc.user_id user_id, count(1) AS `value` FROM car mc inner join users FOR SYSTEM_TIME AS OF mc.proctime as u on mc.user_id=s.id group by mc.user_id 总结
总体来讲,关联维表有四个基础的方式:
(1)查找外部数据源关联
(2)预加载维表关联(内存,状态)
(3)冷热数据储备(算是1和2的结合使用)
(4)维表变更日志关联(广播也好,其他方式的流关联也好)
「同时考虑:」 吞吐量,时效性,外部数据源的负载,内存资源,解耦性等等方面。
四种join方式不存在绝对的一劳永逸,更多的是针对业务场景在各指标上的权衡取舍,因此看官需要结合场景来选择适合的。
来源:http://www.techweb.com.cn/cloud/2022-01-11/2873446.shtml
图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园