摘抄别的博主的博客主要总去CSDN看不太方便自己整理一下加深记忆!
导入文件至数据库
#将脚本导入 source 加文件路径
mysql> source /backup/test.sql;

select
显示表格中的一个或者多个字段中所有的信息
#语法:
select 字段名 from 表名;
示例1:
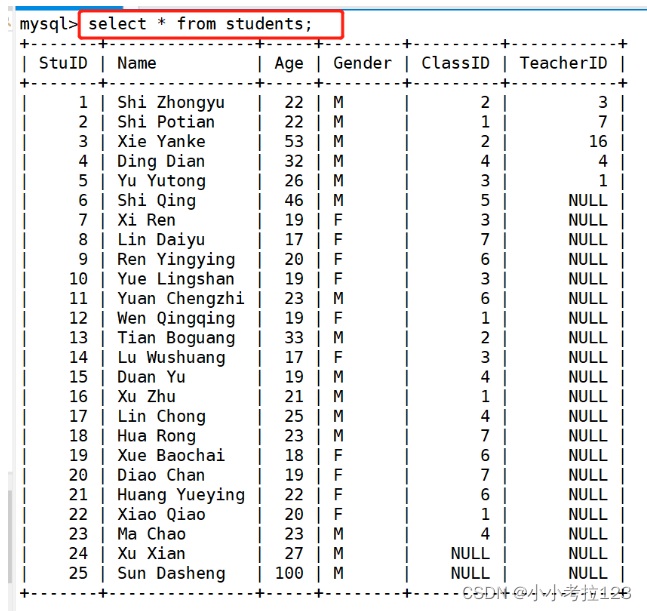
select * from students;
示例2:
select * from students;
distinct
查询不重复记录
#语法:
select distinct 字段 from 表名﹔
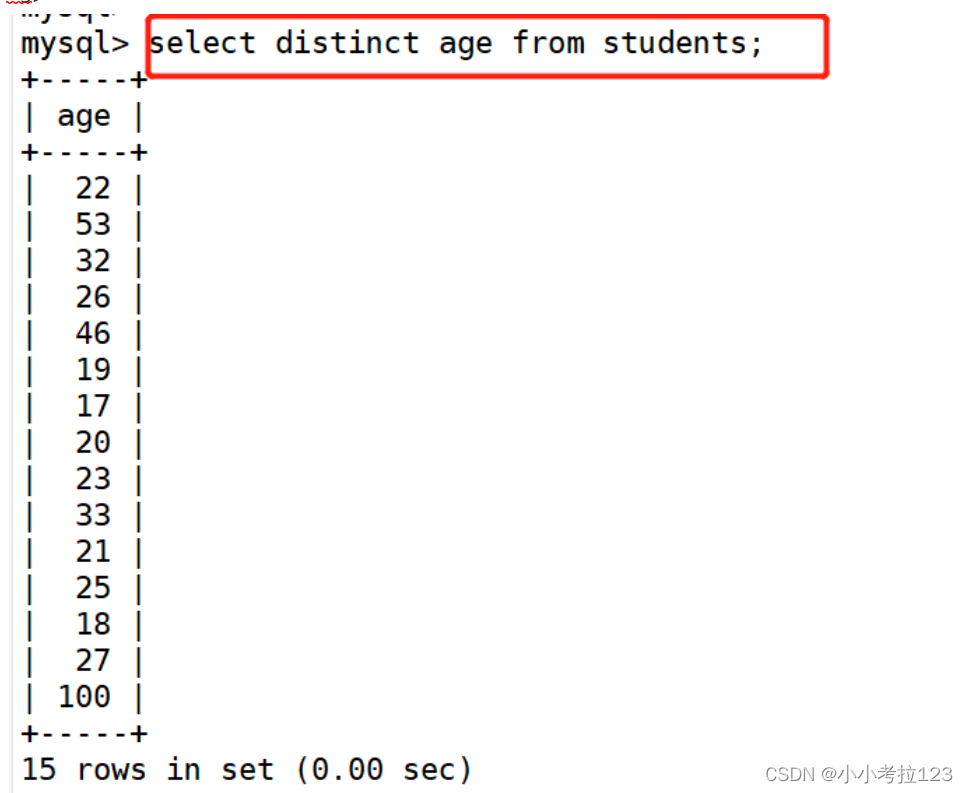
#示例1:去除年龄字段中重复的
select distinct age from students;
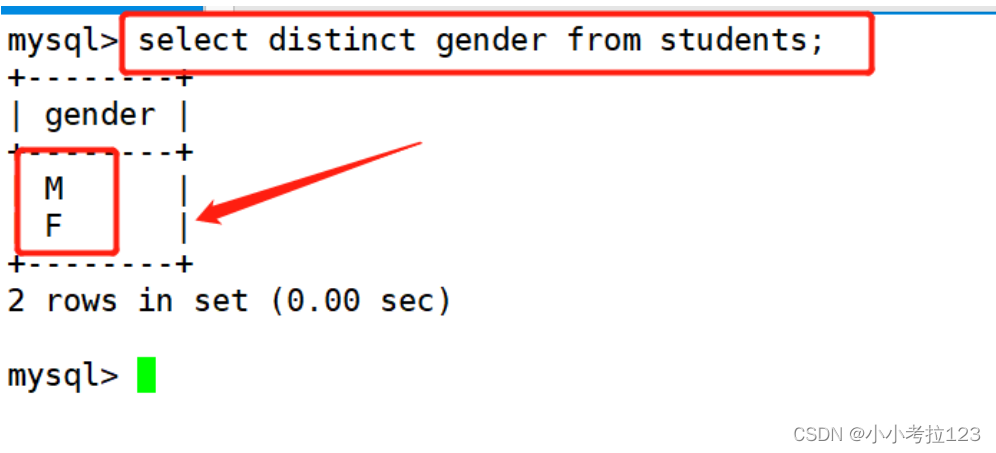
#示例2:查找性别
select distinct gender from students;
where
where 有条件的查询
#语法:
select \'字段\' from 表名 where 条件
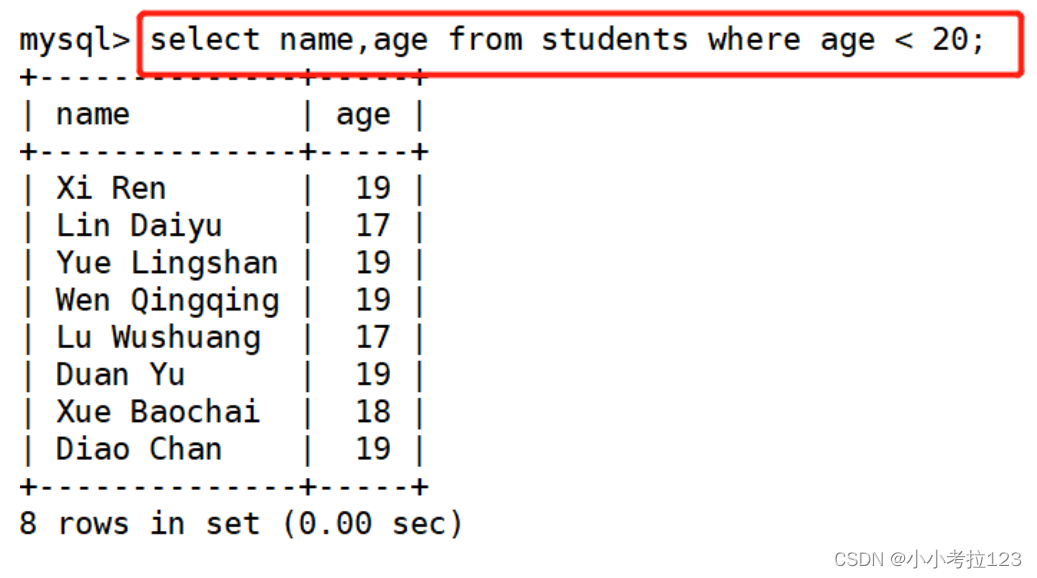
#示例:显示name和age 并且要找到age小于20
select name,age from students where age < 20;
#示例:显示name和age 并且要找到age小于20
select name,age from students where age < 20;
and;or
and 且 ; or 或
#语法:
select 字段名 from 表名 where 条件1 (and|or) 条件2 (and|or)条件3;
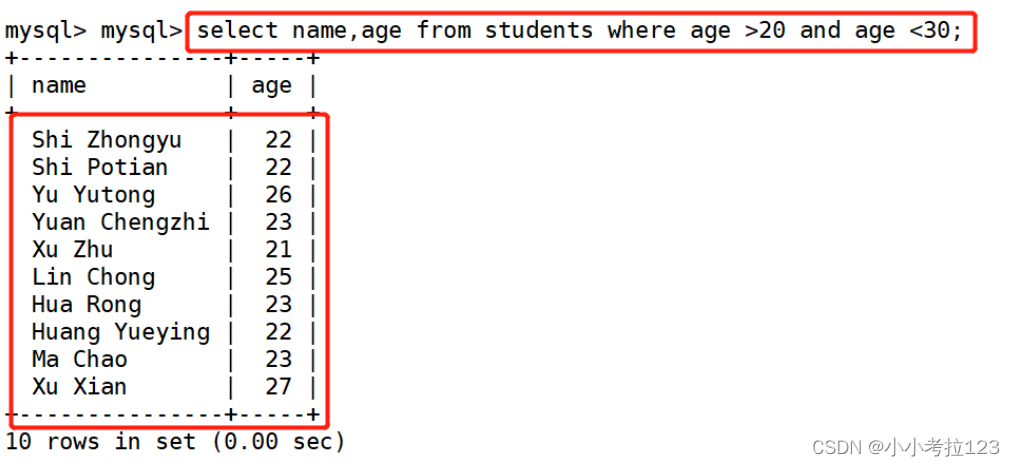
示例1:显示name和age 并且要找到age大于20小于30
select name,age from students where age >20 and age <30;
in
显示已知值的资料
#语法:
select 字段名 from 表名 where 字段 in (\'值1\',\'值2\'....);
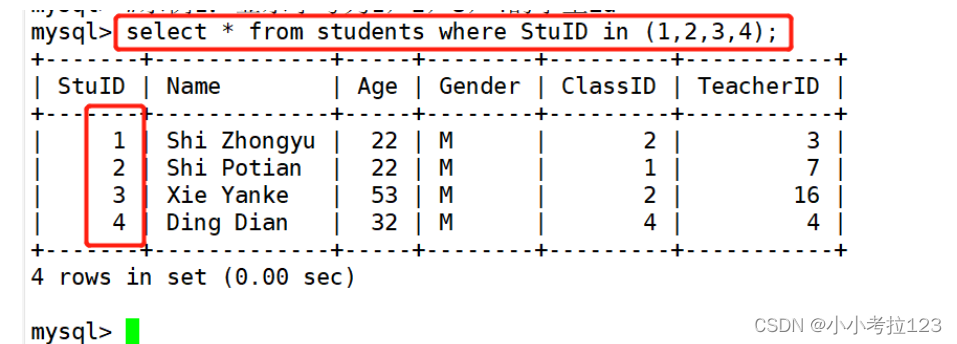
#示例1:显示学号为1,2,3,4的学生记录
select * from students where StuID in (1,2,3,4);
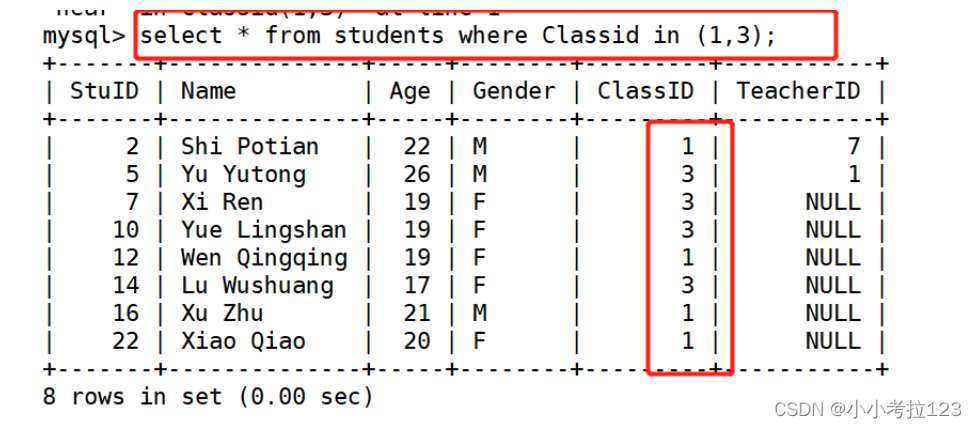
#示例2:显示班级为1和3的学生记录
select * from students where ClassID in (1,3);
between
显示两个值范围内的资料
#语法:
select 字段名 from 表名 where 字段 between \'值1\' and \'值2\';
包括 and两边的值
#示例1:显示学生姓名在Ding Dian和Hua Rong中的学生记录
select * from students where name between \'ding dian\' and \'Hua Rong\';

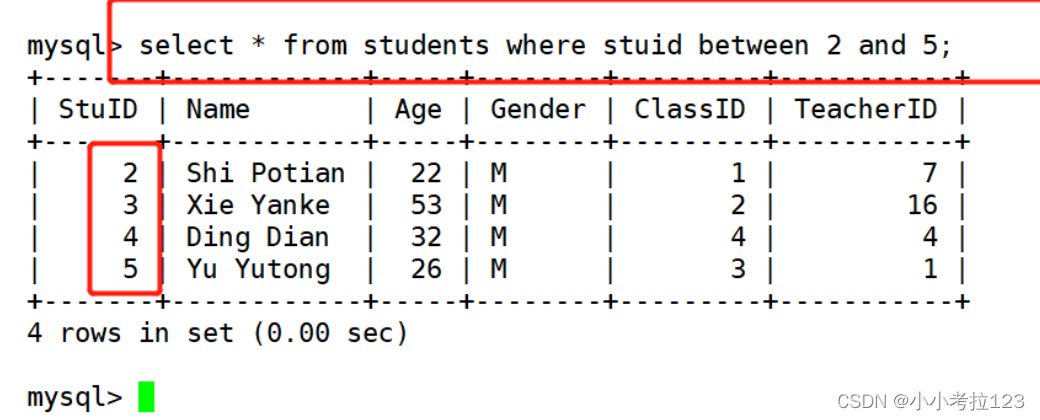
#示例2:显示学生号码id在2-5 的信息
select * from students where stuid between 2 and 5;
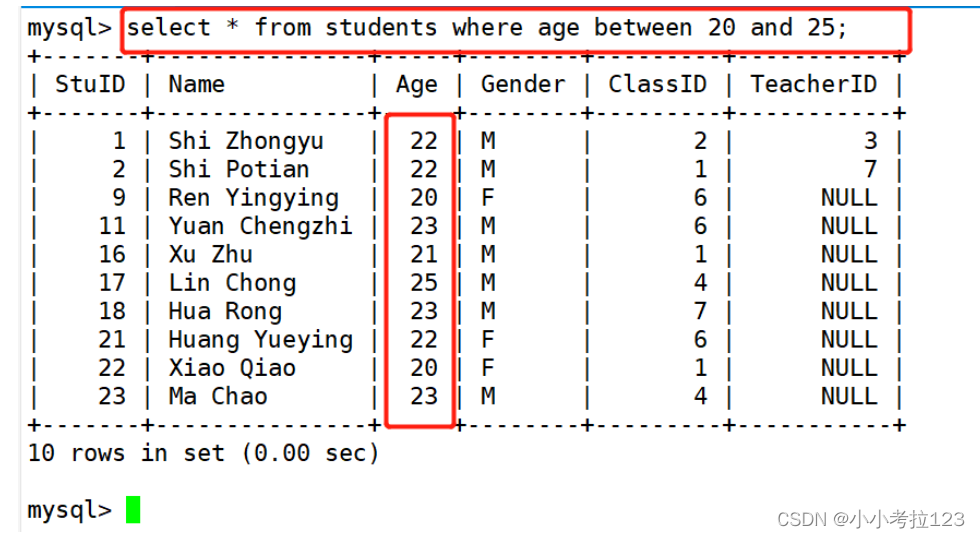
#示例3:显示学生年龄在20-35之间的信息,不需要表中一定有该字段,只会将20到25 已有的都显示出来
select * from students where age between 20 and 25;
like 通配符
通配符通常是和 like 一起使用
#语法:
select 字段名 from 表名 where 字段 like 模式
含义
| % | 表示零个,一个或者多个字符 |
| _ | 下划线表示单个字符 |
| A_Z | 所有以A开头 Z 结尾的字符串 \'ABZ\' \'ACZ\' \'ACCCCZ\'不在范围内 下划线只表示一个字符 AZ 包含a空格z |
| ABC% | 所有以ABC开头的字符串 ABCD ABCABC |
| %CBA | 所有以CBA结尾的字符串 WCBA CBACBA |
| %AN% | 所有包含AN的字符串 los angeles |
| _AN% | 所有 第二个字母为 A 第三个字母 为N 的字符串 |
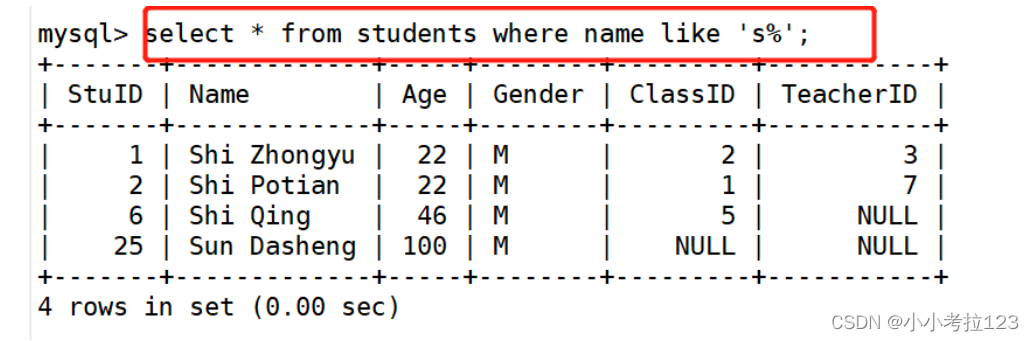
#示例1:查找名字以s开头的学生记录
select * from students where name like \'s%\';
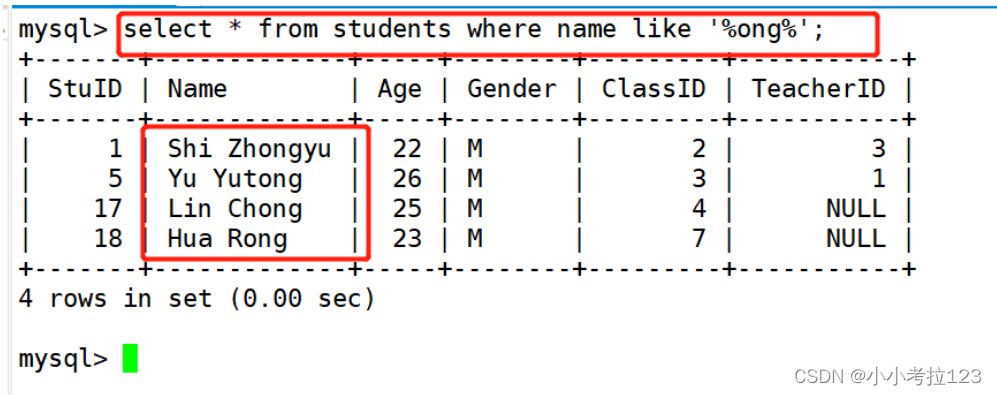
#示例2:查找名字包含ong的学生记录
select * from students where name like \'%ong%\';
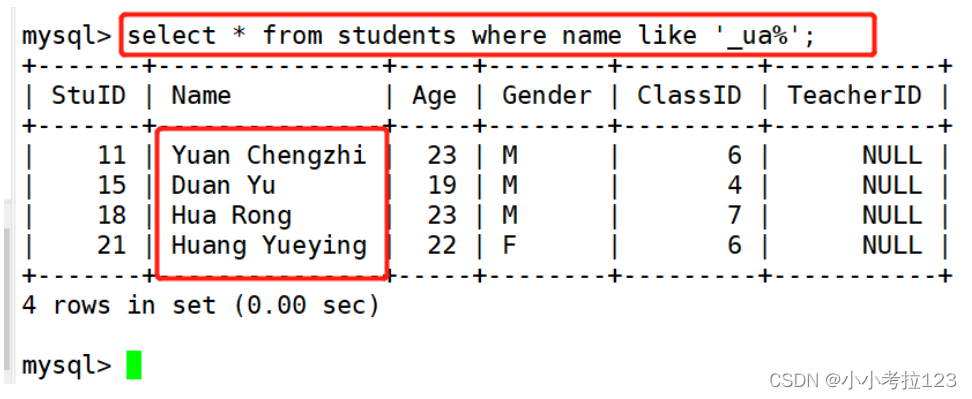
#示例3:查找名字第二个字母为u,第三个字母为a的学生记录
select * from students where name like \'_ua%\';
order by
order by 按关键字排序
#语法:
select 字段名 from 表名 where 条件 order by 字段 [asc,desc];
asc :正向排序
desc :反向排序
默认是正向排序
#示例1:按学生的年龄正向排序显示年龄和姓名字段
select age,name from students order by age;

#示例2:按学生的年龄反向排序显示年龄和姓名字段
select age,name from students order by age desc;
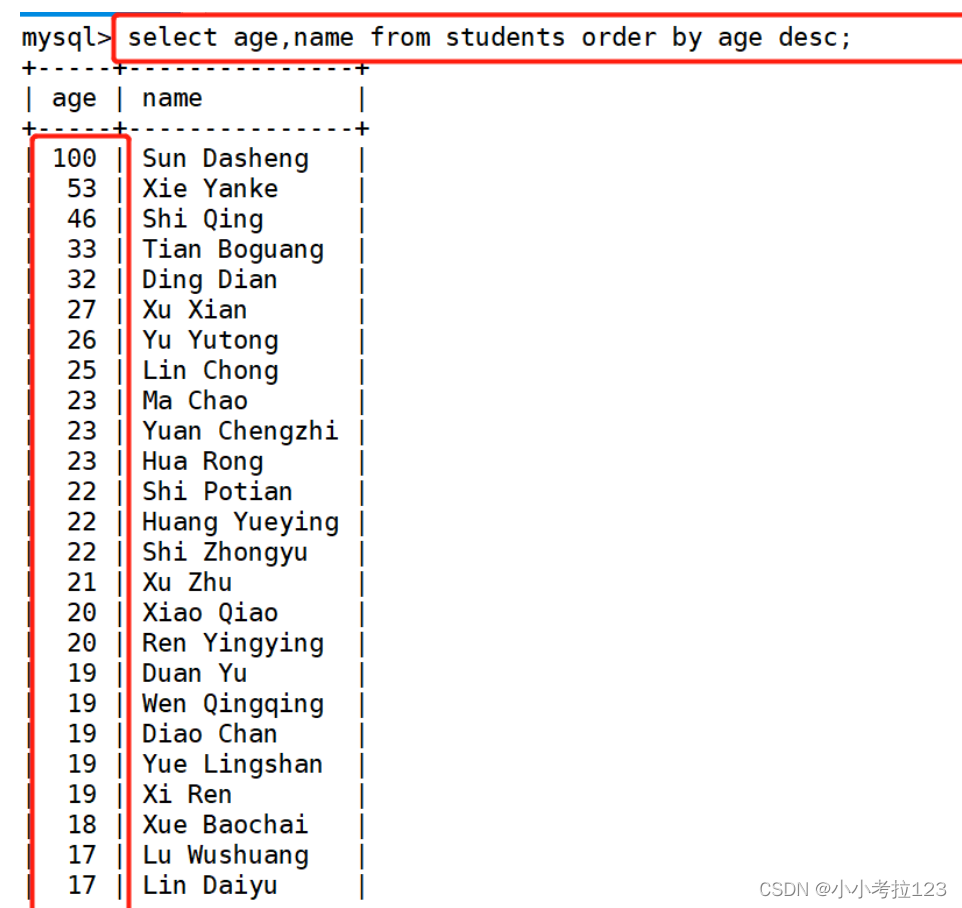
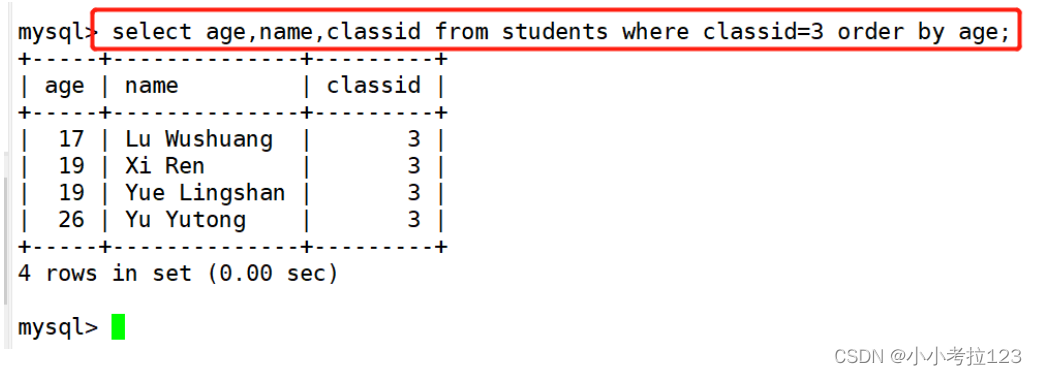
#示例3:显示name、age和classid字段的数据 并且只显示classid字段为3 的 并且以age字段排序
select age,name,classid from students where classid=3 order by age;
函数
数学函数
函数含义
| abs(x) | 返回x 的 绝对值 |
| rand() | 返回0到1的随机数 |
| mod(x,y) | 返回x除以y以后的余数 |
| power(x,y) | 返回x的y次方 |
| round(x) | 返回离x最近的整数 |
| round(x,y) | 保留x的y位小数四舍五入后的值 |
| sqrt(x) | 返回x的平方根 |
| truncate(x,y) | 返回数字 x 截断为 y 位小数的值 |
| ceil(x) | 返回大于或等于 x 的最小整数 |
| floor(x) | 返回小于或等于 x 的最大整数 |
| greatest(x1,x2.....) | 返回返回集合中最大的值 |
| least(x1,x2..........) | 返回返回集合中最小的值 |
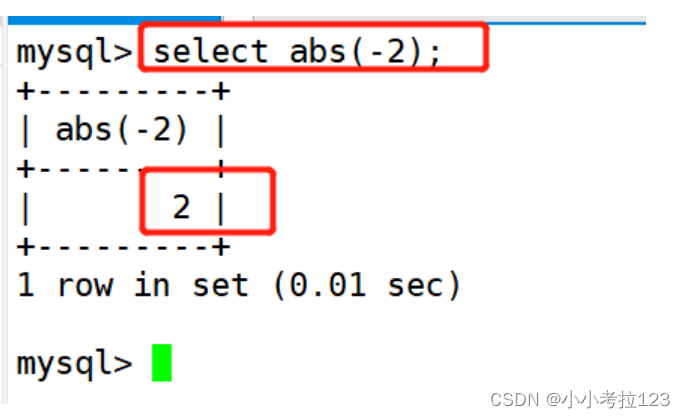
#示例1:返回-2的绝对值
select abs(-2);
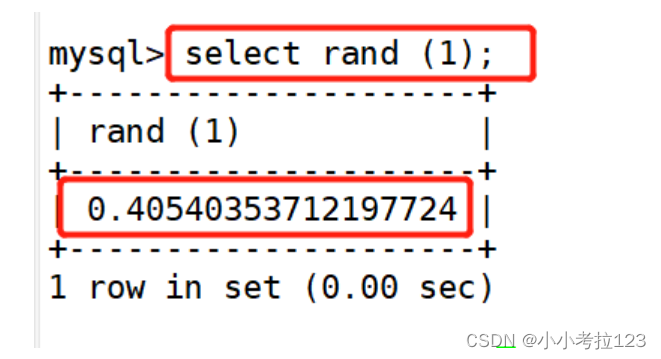
#示例2:随机生成一个数
select rand (1);
#示例3:随机生成排序
select * from students order by rand();

#示例4:返回7除以2以后的余数
select mod(7,2);

#示例5:返回2的3次方
select power(2,3);

#示例6:返回离2.6最近的数
select round(2.6);
#返回离2.4最近的数


#示例7:保留2.335321的3位小数四舍五入后的值
select round(2.335321,2);

#示例8:返回数字 2.335321 截断为2位小数的值
select truncate(2.335321,2);

#示例9:返回大于或等于2.335321 的最小整数
select ceil(2.335321);

#示例10:返回小于或等于 2.335321 的最大整数
select floor(2.335321);

#示例11:返回集合中最大的值
select greatest(1,4,3,9,20);

#示例12:返回集合中最小的值
select least(1,4,3,9,20);

聚合函数
函数含义
| avg() | 返回指定列的平均值 |
| count() | 返回指定列中非 NULL 值的个数 |
| min() | 返回指定列的最小值 |
| max() | 返回指定列的最大值 |
| sum(x) | 返回指定列的所有值之和 |
#示例1:求表中年龄的平均值
select avg(age) from students;

#示例2:求表中年龄的总和
select sum(age) from students;

#示例3:求表中年龄的最大值
select max(age) from students;

#示例4:求表中年龄的最小值
select min(age) from students;

#示例5:求表中有多少班级字段非空记录
select count(classid) from students;
count(明确字段):不会忽略空记录


#示例6:求表中有多少条记录
select count(*) from students;
count(*)包含空字段,会忽略空记录

#示例7:看空格字段是否会被匹配
insert into students values(26,\' \',28,\'f\',1,8);

字符串函数
函数描述
| trim() | 返回去除指定格式的值 |
| concat(x,y) | 将提供的参数 x 和 y 拼接成一个字符串 |
| substr(x,y) | 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始的字符串,跟substring()函数作用相同 |
| substr(x,y,z) | 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始长度为z 的字符串 |
| length(x) | 返回字符串 x 的长度 |
| replace(x,y,z) | 将字符串 z 替代字符串 x 中的字符串 y |
| upper(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成大写字母 |
| lower(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成小写字母 |
| left(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的前 y 个字符 |
| right(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的后 y 个字符 |
| repeat(x,y) | 将字符串 x 重复 y 次 |
| space(x) | 返回 x 个空格 |
| strcmp(x,y) | 比较 x 和 y,返回的值可以为-1,0,1 |
| reverse(x) | 将字符串 x 反转 |
1)trim
语法:
select trim (位置 要移除的字符串 from 字符串)
其中位置的值可以是
leading(开始)
trailing(结尾)
both(起头及结尾)
#区分大小写
要移除的字符串:从字符串的起头、结尾或起头及结尾移除的字符串,缺省时为空格。
#示例1:从名字开头的开始,移除Sun Dasheng中的Sun显示
select trim(leading \'Sun\' from \'Sun Dasheng\');

#示例2:去除空格
select trim(both from \' zhang san \');

2)length
#语法:
select length(字段) from 表名;
#示例:计算出字段中记录的字符长度
select name,length(name) from students;

3)replace
#语法:
select replace(字段,\'原字符\'\'替换字符\') from 表名;
select replace(name,\'ua\',\'hh\') from students;


4)concat
#语法:
select concat(字段1,字段2)from 表名
#示例1:将name,classid字段拼接成一个字符串
select concat(name,classid) from students;

#示例2:只显示3ban的名字和classid为一个组合记录
select concat(name,classid) from students where classid=3;

#示例3:中间加制表符
select concat(name,\'\\t\',classid) from students where classid=3;

4)substr
#语法:
select substr(字段,开始截取字符,截取的长度) where 字段=\'截取的字符串\'
#示例1:截取第6个字符往后
select substr(name,6) from students where name=\'Yue Lingshan\';

#示例2:截取第6个字符往后的两个字符
select substr(name,6,2) from students where name=\'Yue Lingshan\';

group by
对group by 后面的字段的查询结果进行汇总分组,通常是结合聚合函数一起使用的
group by 有一个原则,就是select 后面的所有列中,没有使用聚合函数的列必须出现在 group by 的后面。
#语法:
select 字段1,sum(字段2) from 表名 group by 字段1;
#示例1:求各个班的年龄总和
select classid,sum(age) from students group by classid;

#示例2:求各个班的平均年龄
select classid,avg(age) from students group by classid;

#示例3:根据年龄查看每个班的人数
select classid,count(age) from students group by classid;

having
having:用来过滤由group by语句返回的记录集,通常与group by语句联合使用
having语句的存在弥补了where关键字不能与聚合函数联合使用的不足。如果被SELECT的只有函数栏,那就不需要GROUP BY子句。
要根据新表中的字段,来指定条件
#语法:
SELECT 字段1,SUM(\"字段\")FROM 表格名 GROUP BY 字段1 having(函数条件);
#示例:查看各个班的平均年龄在30以上的班级
select classid,avg(age) from students group by classid having avg(age) > 30;


别名
栏位別名 表格別名
v#语法:
SELECT \"表格別名\".\"栏位1\" [AS] \"栏位別名\" FROM \"表格名\" [AS] \"表格別名\";
#示例:设置表名别名为f,基于班级号来统计各班年龄总和,sum(age)定义别名为total age
select f.classid,sum(age) \'total age\' from students as f group by f.classid;

连接查询
1)inner join(等值相连)
只返回两个表中联结字段相等的行
SELECT * FROM students A INNER JOIN scores B on A.stuid = B.stuid;

2)left join(左联接)
返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中联结字段相等的记录
select * from scores A left join students B on A.stuid = B.stuid;


3)right join(右联接)
select * from scores A right join students B on A.stuid = B.stuid;

子查询
连接表格,在WHERE 子句或HAVING 子句中插入另一个SQL语句
语法:
SELECT \"栏位1\" FROM \"表格1\" WHERE \"栏位2\" [比较运算符]
#外查询
(SELECT \"栏位1\" FROM \"表格1\" WHERE \"条件\");
#示例:查询学生学号为1的得分总和
select sum(score) from scores where stuid in (select stuid from students where stuid=1);

EXISTS
用来测试内查询有没有产生任何结果类似布尔值是否为真
如果有的话,系统就会执行外查询中的SQL语句。若是没有的话,那整个 SQL 语句就不会产生任何结果。
#语法:
SELECT \"栏位1\" FROM \"表格1\" WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM \"表格2\" WHERE \"条件\");
#示例1:先看students表中是否有stuid为1的学生,如果有则执行将scores表中的score求和
select sum(score) from scores where exists (select * from students where stuid=1);


#示例2:先看students表中是否有stuid为88的学生,如果有则执行将scores表中的score求和
select sum(score) from scores where exists (select * from students where stuid=88);

来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/arrorzz/p/15710785.html
图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园