一、多表查询
1.1 数据准备
-- 建表
create table dep(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
);
create table emp(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex enum(\'male\',\'female\') not null default \'male\',
age int,
dep_id int
);
-- 插入数据
insert into dep values
(200,\'技术\'),
(201,\'人力资源\'),
(202,\'销售\'),
(203,\'运营\'),
(205,\'保洁\');
insert into emp(name,sex,age,dep_id) values
(\'jason\',\'male\',18,200),
(\'egon\',\'female\',48,201),
(\'kevin\',\'male\',18,201),
(\'nick\',\'male\',28,202),
(\'owen\',\'male\',18,203),
(\'jerry\',\'female\',18,204);
如何查询jason所在的部门名称?
首先,涉及到SQL查询题目,一定要先明确到底需要几张表。
先查询jason所在的部门编号
select dep_id from emp where name=\'jason\';
根据部门编号查询部门名称
select name from dep where id=(select dep_id from emp where name=\'jason\');
一条SQL语句的查询结果既可以看成是一张表也可以看成是查询条件。
补充:
MySQL的两种注释语法:
-
# 注释
-
-- 注释
1.2 多表查询思路
-
子查询
即将SQL语句的结果当做另外一条SQL语句的查询条件,对应到日常生活中就是我们常见的解决问题的方式:分步操作
-
连表操作:通过连接将需要使用到的表拼接成一张大表,之后基于单表查询完成
- inner join:内连接
- left join:左连接
- right join:右连接
- union:全连接
涉及到多表查询的时候,为了避免表字段重复,需要在字段名的前面加上表名限制,及使用表名.字段名的方式加以区分。
-- inner join:只拼接两张表中共有的部分(有对应关系)
select * from emp inner join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id;
-- left join:以左表为基准展示所有的内容,没有的用NULL填充
select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id;
-- right join:以右表为基准展示所有的内容,没有的用NULL填充
select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id;
-- union:左右表所有的数据都在 没有的用NULL填充
select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id
union
select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id;
\"\"\"
疑问:上述操作一次只能连接两张表 如何做到多张表?
将两张表的拼接结果当成一张表与跟另外一张表做拼接
依次往复 即可拼接多张表
\"\"\"
上述操作一次只能连接两张表,那如何做到连接多张表?
其实只需要遵循子查询的思路就可以,即将两张表的拼接结果当成一张表再与另外一张表做拼接即可,以此往复,即可拼接多张表。
二、Navicat可视化软件
Navicat内部封装了很多SQL的操作,大部分操作用户只需要使用鼠标点点的方式就能完成,其内部会自动构建SQL语句并执行。
以下是关于这款软件的下载与详细使用教程:
MySQL可视化软件:Navicat的下载与使用
三、多表查询练习题
现设有如下五张表,其涉及到的字段名称和所建立的表关系如下图所示:
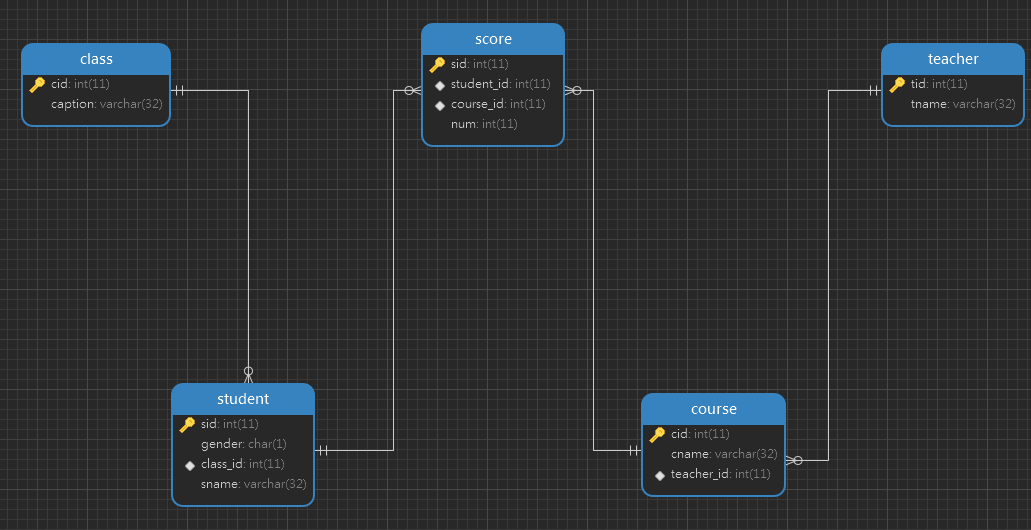
- class表对student表:一对多
- student表对course表:多对多,两者表关系记录在score表中。
- teacher表对course表:一对多
编写较为复杂的SQL语句不要想着一次性写完,可以边写边看。
-- 1、查询所有的课程的名称以及对应的任课老师姓名
SELECT
teacher.tname,
course.cname
FROM
teacher
INNER JOIN course ON teacher.tid = course.teacher_id;
-- 2、查询平均成绩大于八十分的同学的姓名和平均成绩
SELECT
student.sname,
AVG( num )
FROM
score
INNER JOIN student ON student.sid = score.student_id
GROUP BY
student_id
HAVING
AVG( num ) > 80;
-- 子查询:
-- 1.1 按照学生id分组并获取平均成绩
select student_id,avg(num) from score group by student_id;
-- 1.2 筛选出平均成绩大于80的数据 (针对聚合函数的字段结果 最好起别名防止冲突)
select student_id,avg(num) as avg_num from score group by student_id having avg(num) > 80;
-- 1.3 将上述SQL的结果与student表拼接
SELECT
student.sname,
t1.avg_num
FROM
student
INNER JOIN ( SELECT student_id, avg( num ) AS avg_num FROM score GROUP BY student_id HAVING avg( num ) > 80 ) AS t1 ON student.sid = t1.student_id;
-- 3、查询没有报李平老师课的学生姓名
-- 1.先查询李平老师教授的课程编号
select course.cid from course where teacher_id = (select tid from teacher where tname =\'李平老师\');
-- 2.再根据课程id号筛选出所有报了对应课程的学生id号
select distinct score.student_id from score where course_id in (select course.cid from course where teacher_id =
(select tid from teacher where tname =\'李平老师\'));
-- 3.最后去学生表中根据id号取反筛选学生姓名
SELECT
student.sname
FROM
student
WHERE
sid NOT IN (
SELECT DISTINCT
score.student_id
FROM
score
WHERE
course_id IN ( SELECT course.cid FROM course WHERE teacher_id = ( SELECT tid FROM teacher WHERE tname = \'李平老师\' ) )
);
-- 4、查询没有同时选修物理课程和体育课程的学生姓名(只筛选了报了一门课程的,两门和一门没报的都不要)
-- 1.先获取两门课程的id号
select course.cid from course where cname in (\'物理\',\'体育\');
-- 2.然后去分数表中先筛选出所有报了物理和体育课程的学生id(包含两门和一门)
select * from score where course_id in (select course.cid from course where cname in (\'物理\',\'体育\'));
-- 3.再筛选出只报了一门的学生id(按照学生id分组,然后计数,并过滤出计数结果为1的数据)
select score.student_id from score where course_id in (select course.cid from course where cname in (\'物理\',\'体育\')) group by score.student_id having count(score.course_id) = 1;
-- 4.最后根据学生id号去student表中筛选学生姓名
SELECT
student.sname
FROM
student
WHERE
sid IN (
SELECT
score.student_id
FROM
score
WHERE
course_id IN ( SELECT course.cid FROM course WHERE cname IN ( \'物理\', \'体育\' ) )
GROUP BY
score.student_id
HAVING
count( score.course_id ) = 1
);
-- 5、查询挂科超过两门(包括两门)的学生姓名和班级
-- 1.先筛选出小于60分的数据
select * from score where num < 60;
-- 2.再按照学生id分组,统计挂科数量,筛选出挂科超过两门的学生id
select student_id from score where num < 60 group by student_id having count(course_id) >=2;
-- 3.最后通过连接student和class表,查询所需数据
SELECT
student.sname,
class.caption
FROM
class
INNER JOIN student ON class.cid = student.class_id
WHERE
student.sid IN ( SELECT student_id FROM score WHERE num < 60 GROUP BY student_id HAVING count( course_id ) >= 2 );
更多练习可以参考该篇博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/Dominic-Ji/p/10875493.html
四、Python操作MySQL模块:pymysql
4.1 基本使用
该模块为第三方模块,需要下载使用:pip3 install pymysql
import pymysql
# 创建连接,可以连接到MySQL服务端
conn = pymysql.connect(
host=\'127.0.0.1\',
port=3306,
user=\'root\',
password=\'123\',
database=\'db_5\',
charset=\'utf8\'
)
# 生成一个游标对象
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 让数据自动组织成字典
# 定义SQL语句
sql = \'select * from userinfo\'
# 执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 获取返回结果
res = cursor.fetchall()
print(res)
4.2 SQL注入问题
import pymysql
# 创建链接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host=\'127.0.0.1\',
port=3306,
user=\'root\',
password=\'456852\',
database=\'mydb\',
charset=\'utf8\'
)
# 生成一个游标对象
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 让数据自动组织成字典
# 获取用户名和密码
username = input(\'username>>>:\').strip()
password = input(\'password>>>:\').strip()
# 出现问题SQL语句
# sql = \"select * from userinfo where name=\'%s\' and password=\'%s\';\" % (username, password)
# cursor.execute(sql)
# 针对核心数据 不要自己拼接 交由execute方法帮你筛选再拼接
sql = \"select * from userinfo where name=%s and password=%s\"
print(sql)
# 执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql, (username, password))
res = cursor.fetchall()
if res:
print(res)
print(\'登录成功\')
else:
print(\'用户名或密码错误\')
SQL注入问题的产生,是由于特殊符号的组合会产生特殊的效果,从而避免常规的逻辑。
在实际生活中,尤其是在注册用户名的时候,会非常明显的提示你很多特殊符号不能用,其内部原因也是一样的。
结论:
涉及到敏感数据部分,尽量不要自己拼接,交给现成的方法拼接即可;
SQL注入问题的解决方式:execute方法自动帮你解决;
4.3 功能补充
import pymysql
# 创建链接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host=\'127.0.0.1\',
port=3306,
user=\'root\',
password=\'456852\',
database=\'mydb\',
charset=\'utf8\',
autocommit=True # 涉及到增删改 自动二次确认
)
# 生成一个游标对象
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 让数据自动组织成字典
sql1 = \'select * from userinfo\'
sql2 = \'insert into userinfo(name,password) values(%s,%s)\'
sql3 = \'update userinfo set name=\"jasonNB\" where id=1\'
sql4 = \'delete from userinfo where id=2\'
# 1.查询语句可以正常执行并获取结果
# cursor.execute(sql1)
# 2.插入语句能够执行 但是并没有影响表数据
# cursor.execute(sql2,(\'jackson\',666))
# 3.更新语句能够执行 但是并没有影响表数据
# res = cursor.execute(sql3)
# print(res)
# 4.删除语句能够执行 但是并没有影响表数据
# res = cursor.execute(sql4)
# print(res)
\'\'\'针对增删改操作 需要二次确认才可生效\'\'\'
# cursor.execute(sql2,(\'jackson\',666))
# conn.commit()
# cursor.execute(sql3)
# conn.commit()
# cursor.execute(sql4)
# conn.commit()
# 执行多次SQL语句
cursor.executemany(sql2, [(\'jason111\', 123), (\'jason222\', 321), (\'jason333\', 222)])
# 主动关闭链接 释放资源
# conn.close()
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/JZjuechen/p/15929638.html
图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园