Mybatis的环境搭建与入门程序
环境搭建
搭建参考
注意事项:虽然配置好了,但是在IDEA中创建新的文件项目时,会默认绑定IDEA自带的Maven版本,此时则需要进行调整
具体操作流程:文件---->新项目设置---->Maven---->进行配置---->Maven项展开选定正在导入---->将自动下载全部勾选,然后JDK环境选择本地安装的
入门程序(参考:实训报告1)
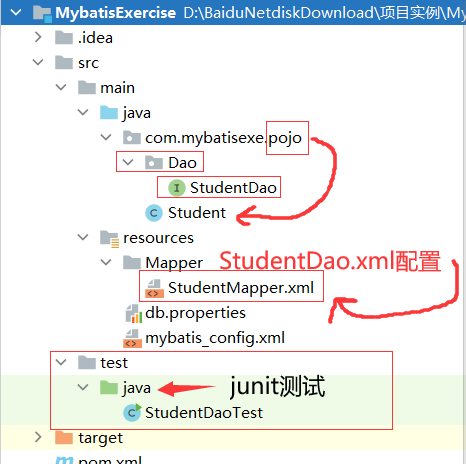
1.IDEA中新建一个Maven项目
2.配置pom.xml文件
<!--此处配置的是环境所需的依赖文件,具体如下-->
<dependencies>
<!--配置Mysql依赖项-->
<dependence>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>xxxx</version>
</dependence>
<!--配置Mybatis依赖项-->
<dependence>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<arifactId>mybatis-migrations</arifactId>
<version>XXXX</version>
</dependence>
<!--配置Junit依赖项-->
<dependence>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<arifactId>junit</arifactId>
<version>XXXX</version>
</dependence>
</dependencies>3.配置数据库文件
需要用到.properties后缀的文件
什么是properties文件?
后缀properties是一种属性文件。
这种文件以key=value格式存储内容
Java中可以使用Properties类来读取这个文件
String value=p.getProperty(key);
就能得到对应的数据
一般这个文件作为一些参数的存储,代码就可以灵活一点
用于适应多语言环境,随着系统的语言环境的变化,读取不同的属性文件,显示对应语言的UI
当配置文件用,在里面读取一些关于路径方面的设置(如ant中的build.properties)
存放一组配置.(类似win下ini, 还要简单些, 因为没有section)
由于难以表达层次, 复杂点可以用xml做配置.
通俗点讲就相当于定义一个变量,在这个文件里面定义这些变量的值,在程序里面可以调用这些变量,好处就 是,如果程序中的参数值需要变动,直接来改这个.property文件就可以了,不用在去修改源代码。
优点在于有利于你以后的代码重构,维护方便
db.properties
mysql.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mysql.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost3306/数据库名?useSSL=False or True&Timezone=设置所需时区
mysql.username=你的Mysql用户名
mysql.password=你的Mysql密码4.配置好pom.xml文件和db.properties文件后,再配置mybatis_config.xml
<!--头部文件,固定且不可更改-->
<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC \"-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN\"
\"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd\">
<!--config配置-->
<configuration>
<!--引入Mysql配置数据-->
<properties resource=\"db.properties\"></properties>
<!--配置Mybatis环境-->
<enviroments default=\"development\">
<environment id=\"development\">
<transactionManager type=\"JDBC\"></transactionManager>
<dataresource type=\"POOLED\">
<!--建立&读取配置参数-->
<property name=\"driver\" value=\"${mysql.driver}\"/>
<property name=\"url\" value=\"${mysql.url}\"/>
<property name=\"username\" value=\"${mysql.username}\"/>
<property name=\"password\" value=\"${mysql.password}\"/>
</dataresource>
</environment>
</enviroments>
</configuration>5.建立Class类与数据库相互映射
public class Student{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String gender;
private String phone;
//自动生成Getter和Setter方法
}6.建立Dao层(持久层),封装各种方法
public interface studentDao{
//接口类中,建立查询学生id方法:selectStudentById(参数类型,字段)
Student selectStudentById(Integer id)
}7.配置StudentMapper(StudentDao).xml文件
<!--头部文件,固定且不可更改-->
<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC \"-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN\"
\"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd\">
<!--建立Dao接口类的映射
Mybatis中<mapper>节点中的namespace是什么意思?
在mybatis中,映射文件中的namespace是用于绑定Dao接口的,即面向接口编程。
当你的namespace绑定接口后,你可以不用写接口实现类,mybatis会通过该绑定自动
帮你找到对应要执行的SQL语句
-->
<mapper namespace=\"com.mybatiesexe.pojo.Dao.StudentDao\">
<!--建立Sql语句
Mybatis中<select>节点中的resultType属性
resultType指的就是“封装查询结果的数据的类型”,也可以理解为“抽象方法的返回值的类型”
-->
<select id=\"与Dao方法对应\" parameterType=\"与Dao方法参数类型对应\" resultType=\"com.mybatisexe.pojo.Student\">
select * from tbstudent where id= #{id}
</select>
</mapper>8.建立StudentTestDao类进行Junit单元测试
public class StudentTestDao{
public static void main(String[] args){
/*什么是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder?
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder用于创建SqlSessionFacoty,SqlSessionFacoty一旦创建完成就
不需要SqlSessionFactoryBuilder了,因为SqlSession是通过SqlSessionFactory创建的。
所以可以将SqlSessionFactoryBuilder当成一个工具类使用,最佳使用范围是方法范围即方法体内局部变量。
*/
//读取已经配置好的Mybatis文件
Reader reader = Resource.getResourceAsReader(\"mybatis_config.xml\");
/*什么是SqlSessionFactory?
SqlSessionFactory是一个接口,接口中定义了openSession的不同重载方法,SqlSessionFactory的最佳使用范围是整个应用运行期间,一旦创建后可以重复使用,通常以单例模式管理SqlSessionFactory。
*/
//New一个SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//通过以上创建的Builder将读取的配置reader传给Factory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(reader);
/*什么是SqlSession?
SqlSession是一个面向用户的接口,sqlSession中定义了数据库操作方法。
每个线程都应该有它自己的SqlSession实例。SqlSession的实例不能共享使用,它也是线程不安全的。因此最佳的范围是请求或方法范围。绝对不能将SqlSession实例的引用放在一个类的静态字段或实例字段中。
*/
//通过Factory对象得到SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//执行Sql语句
StudentDao studentDao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Student student = studentDao.selectStudentById(3);
sout(student.getName());
}
}来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/coldheartsgoinbroke/p/15966844.html
本站部分图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园