AQS 基础篇
AQS 源码解读之加锁篇
在 AQS 源码解读之加锁中,线程 A 占用着锁没有释放。然后线程 B 和线程 C 都在 CHL 队列中排队,也就是执行了 parkAndCheckInterrupt 方法将自己挂起了。现在 CHL 队列的状态:
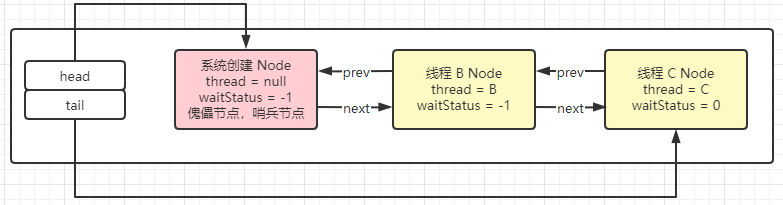
线程 A
unlock() 方法解析
ReentrantLock 类中的 unlock 方法
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}sync 类中的 release 方法
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 主要是修改 state 的值和设置占用锁的线程
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 类中的抽象 tryRelease 方法
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}sync 类中的具体实现
// releases = 1
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// 获取 state 的值,之前被线程 A 设置成 1 现在一减等于 0
int c = getState() - releases;// c = 0
// 判断当前线程是否等于占用锁的线程
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// c = 0 条件成立
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
// 将当前占用锁的线程设置成 null
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
// 将 AQS 中 state 的值设置成 0
setState(c);
// 返回 true
return free;
}sync 类中的 release 方法
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 主要是修改 state 的值和设置占用锁的线程
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// head 现在指向的是傀儡节点
Node h = head;
// 通过上面的图可得 h.waitStatus = -1
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}unparkSuccessor(h)
// node 等于傀儡节点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
// node.waitStatus; = -1
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
// 通过比较并修改将傀儡节点的 waitStatus 的值改成 0
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
// 傀儡节点的后指针指向的是线程 B 对应的 Node 节点
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
// 调用 unpark 方法唤醒挂起的线程 B
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}总结
- 线程 A 调用 unlock 方法,主要就做了三件事:
- 第一件事就是将 AQS 中的变量 state 修改成 0;
- 第二件事就是将占用线程的 exclusiveOwnerThread 修改为 null;
- 第三件事就是唤醒 CLH 队列中被阻塞的指定线程。
线程 B
在 AQS 源码解读之加锁中,线程 B 执行了 parkAndCheckInterrupt 方法将自己挂起了,然后现在线程 A 执行了 unpark 方法,唤醒了线程 B。现在线程 B 要继续执行后面的代码。
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 线程 B 被挂起在这个地方
LockSupport.park(this);
// 唤醒后判断线程是否被通知中断,否返回 false
return Thread.interrupted();
}acquireQueued
因为是自旋,所以这个时候 acquireQueued 方法还没有执行结束,继续执行下一次循环。
// node:线程 B 对应的 Node 节点 arg = 1
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
// 获取现在队列中的第一个节点也就是系统创建的 Node 节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}tryAcquire
// acquires = 1
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
// 现在是线程 B
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 由于线程 A 已经释放了锁并修改了 state 的值,所以现在等于 0
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
// 通过比较并修改,将 state 的值改成 1
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
// 将占用锁的线程设置成线程 B
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error(\"Maximum lock count exceeded\");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}经过 nonfairTryAcquire 方法的执行,现在线程 B 已经成功占用到锁。
// node:线程 B 对应的 Node 节点 arg = 1
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
// 获取现在队列中的第一个节点也就是系统创建的 Node 节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// tryAcquire 修改成功返回 true
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
// 将 CLH 队列中的头节点设置成线程 B 对应的 Node 节点
setHead(node);
// 将傀儡节点的尾指针设置为 null,为了方便进行垃圾回收
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
// 然后返回 false
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}setHead
private void setHead(Node node) {
// 将头节点的值设置成 线程 B 对应的 Node 节点
head = node;
// 将 Node 节点中的线程设置为 null
node.thread = null;
// 将 Node 节点的前指针设置为 null
node.prev = null;
}经过这些步骤后此时 CLH 队列的情况是:
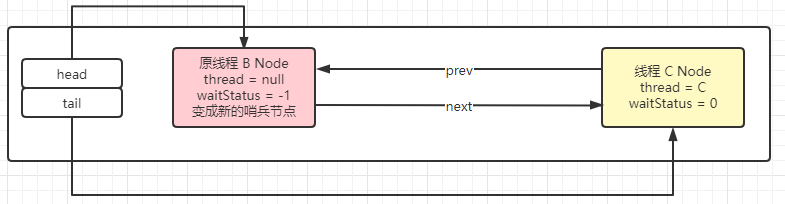
总结
AQS 就是通过 state 和 CLH 来管理线程,其中 lock 方法的主要作用就是查看 state 的值是不是等于 0,如果等于 0,就说没有人占用锁可以直接使用。如果不等于 0 的话就相当于有人占用锁了就需要排队了。
排队的话又牵扯出一个哨兵节点(傀儡节点),CLH 中的 Node 节点,代码会帮我们初始化一个 Node 节点作为哨兵节点,这个值一开始就是我们的头节点与尾节点。后面其他线程的 Node 节点就会直接在其后面进行连接。最后排队的线程会调用 LockSupport.park(this); 将自己挂起,等待其他线程执行完代码后再将自己唤醒。
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/lhnstart/p/16030494.html
本站部分图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园