![]() 容器(可以用来管理所有的组件(类))
容器(可以用来管理所有的组件(类))
核心关注:IOC和AOP
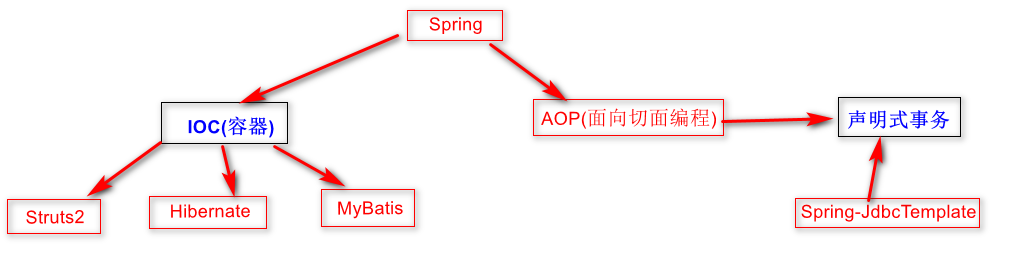
1.IOC
Inversion(反转) Of Control:控制反转
控制:资源的获取方式
1.主动式(要什么资源自己创建)
Person{
Book book=new Book();
Dog dog=new Dog();
//复杂对象的创建时比较庞大的工程
}
2.被动式:资源的获取不是自己创建,而是交给一个容器创建和设置
Person{
Book book;
public void test(){
book.read();
}
}
容器:管理所有的组件(有功能的类),主动的new资源改为被动的接受资源1.1 DI(Dependency Injection)依赖注入
容器能知道哪个组件(类)运行的时候,需要另外一个组件(类);
容器通过反射的形式,将容器中准备好的Book对象注入(利用反射给属性赋值)到Person中IOC只是思想,而DI是具体的实现
代码实现:
1.实体类
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String email;
public Person() {
System.out.println(\"person的构造器!\");
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println(\"设置pserson的name\");
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
System.out.println(\"设置person的age\");
this.age = age;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
System.out.println(\"设置person的gender\");
this.gender = gender;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
System.out.println(\"设置person的email\");
this.email = email;
}
....
...get()
}
2.spring的配置文件ioc.xml
<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?>
<beans xmlns=\"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans\"
xmlns:xsi=\"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance\"
xsi:schemaLocation=\"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd\">
<!--注册person对象,spring会自动创建这个person对象-->
<bean class=\"com.Person\" id=\"person01\">
<property name=\"age\" value=\"18\"></property>------------->name是bean中的属性,通过set方法反射注入
<property name=\"email\" value=\"244594537@qq.com\"/>
<property name=\"gender\" value=\"男\"/>
<property name=\"name\" value=\"吴孟达\"/>
</bean>
</beans>
3.测试类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(\"启动spring容器....\");
ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"ioc.xml\");--------->启动spring的配置文件
System.out.println(\"spring容器启动成功!\");
Person person= (Person) ioc.getBean(\"person01\");----------->此处的person01为spring配置文件中的bean的id
System.out.println(person);
}
}
输出:
启动spring容器....
person的构造器!
设置person的age
设置person的email
设置person的gender
设置pserson的name
spring容器启动成功!
Person{name=\'吴孟达\', age=18, gender=\'男\', email=\'244594537@qq.com\'}
结论:------>发现其执行顺序为:
1.<bean...>元素驱动spring容器调用构造器创建对象
2.<property...>元素驱动spring执行setter方法如果一个实体类中引用了其他实体类,容器加载的执行顺序
1.第一种情况:范围大的(person引用book)在范围小的前面
spring配置文件内容:
<bean id=\"person01\" class=\"entity.Person\">
<property name=\"age\" value=\"18\"></property>
<property name=\"name\" value=\"吴孟达\"></property>
<property name=\"book\" ref=\"book\"/>
</bean>
<bean id=\"book\" class=\"entity.Book\">
<property name=\"name\" value=\"java分析\"/>
<property name=\"price\" value=\"32\"/>
</bean>
实体类信息:
。。。
测试类信息:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(\"加载spring....\");
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"ioc.xml\");
System.out.println(\"spring容器启动成功!\");
Person person= (Person) ac.getBean(\"person01\");
System.out.println(person.toString());
}
输出:
加载spring....
person实例化!
Book实例化!
Book执行set name方法
Book执行set price方法
person执行set age方法
person执行set name方法
spring容器启动成功!
发现执行顺序为:
1.先实例化两个对象
2.在执行小的set方法
3.再执行大的set方法
第二种情况:小范围的在上
spring配置文件内容:
<bean id=\"book\" class=\"entity.Book\">
<property name=\"name\" value=\"java分析\"/>
<property name=\"price\" value=\"32\"/>
</bean>
<bean id=\"person01\" class=\"entity.Person\">
<property name=\"age\" value=\"18\"></property>
<property name=\"name\" value=\"吴孟达\"></property>
<property name=\"book\" ref=\"book\"/>
</bean>
输出:
Book实例化!
Book执行set name方法
Book执行set price方法
person实例化!
person执行set age方法
person执行set name方法
spring容器启动成功!
执行顺序为:
1.小范围对象实例化
2.小范围对象set方法
3.大范围对象实例化
4.大范围对象set方法
2.源码解析
1.
以此为示例:
<bean id=\"book\" class=\"entity.Book\"></bean>
实际上<bean.../>元素默认一反射的方式来调用该类的无参构造器
底层简单源码如下:
String idStr=...;//解析<bean。。。。/>元素的id属性得到该字段的字符串值为\"book\"
String classStr=...;//解析class属性得到该字段的值为:entity.Book
Class clazz=Class.forName(classStr);
Object object=clazz.newInstance();//通过反射示例化对象
container.put(idstr,obj);//将对象放入容器给中,container为spring容器
2.
<bean id=\"person01\" class=\"entity.Person\">
<property name=\"book\" ref=\"book\"/>
</bean>
底层的简单源码如下:
String nameStr=...;解析<property.../>元素的name属性得到该字符串的值为book
String refStr=..;解析<property.../>元素的ref属性得到该字符串的值为book
String setterName-\"set\"+nameStr.subString(0,1).toUpperCase()+name.subString(1);//生成将要调用的setter方法】
Object paramBean=container.get(refStr);//从容器中取到refStr的bean,作为传入参数
Method setter=clazz.getMethod(setterName,parmBean.getClass())//此处的clazz和1的对应起来
setter.incoke(obj,parmBean);//此处的obj和1的对应起来
3.组件在spring容器中是单例的
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(\"加载spring....\");
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"ioc.xml\");
System.out.println(\"spring容器启动成功!\");
Person person1= (Person) ac.getBean(\"person01\");
Person person2= (Person) ac.getBean(\"person01\");
System.out.println(person1==person2);------------------------->此时输出为true;
}
4.使用构造器为bean的属性赋值
spring配置文件为:
<bean id=\"book\" class=\"entity.Book\">
<property name=\"name\" value=\"java分析\"/>
<property name=\"price\" value=\"32\"/>
</bean>
<bean id=\"person01\" class=\"entity.Person\">-------------------------------->此处有两个person的bean:这一个使用set方法给属性赋值,调用的是无参构造器
<property name=\"age\" value=\"18\"></property>
<property name=\"name\" value=\"吴孟达\"></property>
<property name=\"book\" ref=\"book\"/>
</bean>
<bean id=\"person02\" class=\"entity.Person\">------------------------------>这里调用的是有参构造器来进行属性赋值
<constructor-arg name=\"age\" value=\"18\"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name=\"book\" ref=\"book\"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name=\"name\" value=\"吴孟达02\"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
person类的代码:
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Book book;
public Person() {
System.out.println(\"person执行无参构造器\");
}
public Person(String name, Integer age, Book book) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.book = book;
System.out.println(\"person执行有参构造器\");
}
get/set方法
}
测试类方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(\"加载spring....\");
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"ioc.xml\");
System.out.println(\"spring容器启动成功!\");
Person person= (Person) ac.getBean(\"person02\");
System.out.println(person.toString());
}
输出:
加载spring...
Book实例化!
Book执行set name方法
Book执行set price方法
person执行无参构造器-------------->调用无参构造器实例化对象,然后调用set方法赋值
person执行set age方法
person执行set name方法
person执行有参构造器-------------->调用有参构造器,并且直接赋值
spring容器启动成功!
Person{name=\'吴孟达02\', age=18, book=Book{name=\'java分析\', price=32}}
5.使用p名称空间为bean属性赋值
1.在spring的xml文件中加入这一句:xmlns:p=\"http://www.springframework.org/schema/p\"
<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?>
<beans xmlns=\"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans\"
xmlns:xsi=\"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance\"
xmlns:p=\"http://www.springframework.org/schema/p\"----------------------------------->加入这一句
xsi:schemaLocation=\"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd\">
<bean id=\"book\" class=\"entity.Book\">
<property name=\"name\" value=\"java分析\"/>
<property name=\"price\" value=\"32\"/>
</bean>
<bean id=\"person03\" class=\"entity.Person\" p:age=\"18\" p:name=\"吴孟达03\" p:book-ref=\"book\"></bean>------>此时可以通过p标签进行赋值
</beans>
6.复杂赋值
1.给属性赋值null
<bean id=\"person04\" class=\"entity.Person\">
<property name=\"name\">
<null></null>---------------------------->使用null标签进行赋值:不能使用<property name=\"name\" value=\"null\">这是付了一个null的字符串
</property>
</bean>
2.属性是引用时
2.1引用外部bean
<bean id=\"book\" class=\"entity.Book\">
<property name=\"name\" value=\"java分析\"/>
<property name=\"price\" value=\"32\"/>
</bean>
<bean id=\"person04\" class=\"entity.Person\">
<property name=\"name\">
<null></null>
</property>
<property name=\"book\" ref=\"book\"></property>------------->如果外边已经有了像引用的Book bean,则使用ref引用:这里意思是:book=ioc.getBean(\"book\")
</bean>
测试代码:
ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"ioc.xml\");
Person person= (Person) ioc.getBean(\"person04\");
System.out.println(ioc.getBean(\"book\")==person.getBook());------------->此时输出为true
2.2内部引用
<bean id=\"person04\" class=\"entity.Person\">
<property name=\"name\">
<null></null>
</property>
<property name=\"book\">
<!--对象我们可以使用bean标签创建 book=new Book();引用内部bean-->
<bean class=\"entity.Book\">---------------------------------------->此处需要注意的是:内部bean不能直接通过ioc容器获取:
<property name=\"name\" value=\"java\"></property> ----->如<bean id=\"bookInner\" class=\"entity.Book\">内部bean加上id
<property name=\"price\" value=\"25\"></property> ------>ioc.getBean(\"bookInner\")会获取出错!
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
测试代码为:
ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"ioc.xml\");
Person person= (Person) ioc.getBean(\"person04\");
System.out.println(ioc.getBean(\"book\")==person.getBook());------------->此时输出为false
3.为list属性赋值
为psrson新增属性
private List<Book> library;
如何为library赋值
<property name=\"library\">
<!--library=new ArrayLiast<Book>-->
<list>-------------------------------->使用过list标签
<bean class=\"entity.Book\" p:name=\"java\" p:price=\"14\"></bean>------>1.用bean标签创建list元素
<ref bean=\"book\"></ref>-------------------------------------------->2.用ref标签引入外部bean
</list>
</property>
4.为map赋值
为person新增一个属性
private Map map;
springxml中的配置
<property name=\"map\">
<map>-------------------------------------------->使用map标签:map=new HashMap<>();
<entry key=\"key01\" value=\"张三\"></entry>
<entry key=\"key02\" value=\"18\"></entry>
<entry key=\"book01\" value-ref=\"book\"></entry>----->可以使用value-ref引入外部bean
<entry key=\"key04\">
<bean class=\"entity.Person\" p:name=\"吴孟达\" p:age=\"18\" p:book-ref=\"book\"></bean>------>也可以使用该方式引入内部bean
</entry>
<entry key=\"key05\">---->map中嵌套map
<map>
</map>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
5.为Properties赋值
person新增一个属性:
private Properties properties;
spring的配置文件中:
<property name=\"properties\">
<!--properties=new Properties();所有的k=v都是String-->
<props>
<!--k=v都是string,值直接写在标签中-->
<prop key=\"username\">root</prop>
<prop key=\"password\">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
6.使用util名称空间创建集合类型的bean
使用场景:如果相同的map或者list在多处都有引用
可以将map或list单独拿出来做个bean
使用步骤
1.在spring的配置文件中加入:xmlns:util=\"http://www.springframework.org/schema/util\"
<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?>
<beans xmlns=\"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans\"
xmlns:xsi=\"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance\"
xmlns:p=\"http://www.springframework.org/schema/p\"
xmlns:util=\"http://www.springframework.org/schema/util\"---------------------->在spring的配置文件中加入这行
xsi:schemaLocation=\"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd\">
。。。。。
</bean>
2.
<!--相当于new LinkedHashMap<>()-->
<util:map id=\"mymap\">
<!--往map中添加元素-->
<entry key=\"key01\" value=\"张三\"></entry>
<entry key=\"key02\" value=\"18\"></entry>
<entry key=\"book01\" value-ref=\"book\"></entry>
<entry key=\"key04\">
<bean class=\"entity.Person\" p:name=\"吴孟达\" p:age=\"18\" p:book-ref=\"book\"></bean>
</entry>
<entry key=\"key05\">
<map></map>
</entry>
</util:map>
3.其他地方的使用
<property name=\"map\" ref=\"mymap\"></property>----->直接根据引用获取即可
也可以在代码中直接获取
Map<String,Object> map= (Map<String, Object>) ioc.getBean(\"mymap\");
7.util:list的使用和list标签类似
<util:list id=\"mylist\">
<bean class=\"entity.Person\" p:book=\"西游\" p:name=\"吴孟达\"></bean>
<ref bean=\"mymap\"></ref>
<value>12</value>
</util:list>
8.级联属性:属性的属性
<bean id=\"book\" class=\"entity.Book\">
<property name=\"name\" value=\"java分析\"/>
<property name=\"price\" value=\"32\"/>
</bean>
<bean id=\"person05\" class=\"entity.Person\">
<property name=\"book\" ref=\"book\"></property>
<property name=\"book.price\" value=\"1000\"></property>
----->这里通过book.price直接更改:person的book属性的price属性:但这里注意的是这里一改,容器中的book的bean的price属性改为1000
</bean>
9.通过继承实现bean属性的重用
<bean id=\"person01\" class=\"entity.Person\">
<property name=\"age\" value=\"18\"></property>
<property name=\"name\" value=\"吴孟达\"></property>
<property name=\"book\" ref=\"book\"/>
</bean>
这里需要一个personbean,其他属性都一样,只有age属性变为19,则可以这样
<bean id=\"person06\" class=\"entity.Person\" parent=\"person01\">--------->使用parent属性,指定需要继承属性的bean id,这里的继承只是当前bean的配置信息继承,并不是真正的类继承
<property name=\"name\" value=\"刘丹\"></property>
</bean>
结论:
1. 这里的person01和pserson06在容器中是不同的组件(对象)
2.这两个组件的属性都相同,只有name属性值不同
3.因为指定了要继承配置信息的类,所以上述还可以这样写
<bean id=\"person06\" parent=\"person01\">-------------------------->省略了class,因为配置信息继承于person01,所以class配置值可以继承person01的class配置值值
<property name=\"name\" value=\"刘丹\"></property>
</bean>
4.父类的信息不会因为子类而更改!
10.专门建立一个供其他bean继承的bean
<bean id=\"person01\" class=\"entity.Person\" abstract=\"true\">----------------------->加入:abstract=\"true\"
<property name=\"age\" value=\"18\"></property>
<property name=\"name\" value=\"吴孟达\"></property>
<property name=\"book\" ref=\"book\"/>
</bean>
abstract=\"true\"这个bean的配置是一个抽象的,不能获取他的实例,只能被别人继承
此时:
ioc.getBean(\"person01\");-------------------->此时获取会报错,因为这个是被其他bean继承的
7.bean的作用域
1.单例:scope=\"singleton\"
<bean id=\"person05\" class=\"entity.Person\" scope=\"singleton\">
<property name=\"book\" ref=\"book\"></property>
<property name=\"book.price\" value=\"1000\"></property>
</bean>
2.多例:scope=\"prototype\"
<bean id=\"person05\" class=\"entity.Person\" scope=\"prototype\">
<property name=\"book\" ref=\"book\"></property>
<property name=\"book.price\" value=\"1000\"></property>
</bean>
结论:
1.scope=\"singleton\"单例模式:默认
1.1在容器启动完成前就已经创建好对象,保存在容器中
1.2任何获取都是获取之前创建好的对象
2.scope=\"prototype\"多例模式
2.1容器启动默认不会创建多例的bean
2.2每次获取的时候创建这个bean(ioc.getBean(\"person05\"))
2.3每次获取都会创建一个新的对象
8.bean的生命周期(自定义初始化方法和销毁方法)
1.当是单例模式
1.person实体类
public class Person {
//person的无参构造器
public Person() {
System.out.println(\"person的无参构造器方法...\");
}
//自定义初始化方法
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println(\"person的初始化方法\");
}
//自定义对象销毁方法
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println(\"person的销毁方法\");
}
}
2.spring的配置文件
<bean id=\"person\" class=\"entity.Person\"
init-method=\"initMethod\"--------------------------->指定自定义的初始化方法
destroy-method=\"destroyMethod\"--------------------->指定自定义的销毁方法
>
</bean>
3.测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(\"spring容器启动...\");
ConfigurableApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"ioc.xml\");
System.out.println(\"spring容器启动成功!\");
System.out.println(\"关闭spring容器...\");
ioc.close();---------------------------------------->调用容器的停止方法
System.out.println(\"关闭spring容器成功!\");
}
输出:
spring容器启动...
person的无参构造器方法...
person的初始化方法
spring容器启动成功!
关闭spring容器...
person的销毁方法
关闭spring容器成功!
2.当是多例模式
2.1ioc的配置文件
<bean id=\"person\" class=\"entity.Person\"
scope=\"prototype\"---------------------------->多例模式
init-method=\"initMethod\"
destroy-method=\"destroyMethod\"
>
</bean>
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(\"spring容器启动...\");
ConfigurableApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"ioc.xml\");
System.out.println(\"spring容器启动成功!\");
System.out.println(\"关闭spring容器...\");
ioc.close();
System.out.println(\"关闭spring容器成功!\");
}
输出:
spring容器启动...
spring容器启动成功!
关闭spring容器...
关闭spring容器成功!
因为多例模式不是容器启动的时候创创建,而是在ioc.getBean(\"id\")时候创建该对象!
2.2当测试代码为:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(\"spring容器启动...\");
ConfigurableApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"ioc.xml\");
System.out.println(\"spring容器启动成功!\");
ioc.getBean(\"person\");------------------------>多例模式获取bean对象
System.out.println(\"关闭spring容器...\");
ioc.close();
System.out.println(\"关闭spring容器成功!\");
}
输出:
spring容器启动...
spring容器启动成功!
person的无参构造器方法...
person的初始化方法
关闭spring容器...
关闭spring容器成功!
结论:
1.当是单例模式时:Bean的生命周期
(容器启动)构造器方法---->初始化方法----->(容器关闭)销毁方法
2.多实例
获取bean(构造器------>初始化方法---->容器关闭(不会调用销毁方法))
9.Bean的后置处理器
1.自定义一个类实现BeanPostProcessor接口
public class MyBeanPostProcess implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 自定义的初始化方法之前调用
* Object o是容器创建的bean
* String s是spring配置文件中配置的id
*/
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(\"bean的后置处理器Befor...方法\");
System.out.println(s+\":\"+o);
return o;----->注意:这里不能return null,要不会报错
}
//自定义初始化方法之后执行
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(\"bean的后置处理器After...方法\");
System.out.println(s+\":\"+o);
return o;------------------------->注意:这里如果return null;则ioc.getBean也是为null;
}
}
2.在spring配置文件中配置后置处理器
<!--实体类配置-->
<bean id=\"person01\" class=\"entity.Person\"
init-method=\"initMethod\"----------------------->perosn类的自定义初始化方法(person实例化时后会调用)
destroy-method=\"destroyMethod\">----------------->person类的自定义销毁方法(spring容器销毁前会调用)
<property name=\"age\" value=\"18\"></property>
<property name=\"name\" value=\"吴孟达\"></property>
</bean>
<!--后置处理器配置-->
<bean id=\"myBeanPostProcess\" class=\"Test.MyBeanPostProcess\"></bean>
3.测试代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(\"加载spring....\");
ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"ioc.xml\");
System.out.println(\"spring容器启动成功!\");
Object bean= ioc.getBean(\"person01\");
System.out.println(\"容器获取的bean:\"+bean);
}
4.输出:
person执行无参构造器
person执行set age方法
person执行set name方法
bean的后置处理器Befor...方法
person01:Person{name=\'吴孟达\', age=18, book=null}
person自定义的初始化方法
bean的后置处理器After...方法
person01:Person{name=\'吴孟达\', age=18, book=null}
spring容器启动成功!
容器获取的bean:Person{name=\'吴孟达\', age=18, book=null}
结论:
发现带后置处理器的执行流程如下: 执行顺序:
- 1.bean实例化
- 2.执行bean的后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
- 3.执行自定义的初始化方法
- 4.执行bean后置处理器的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/wmd-l/p/16226683.html
本站部分图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园