二刷jdbc
作者小结:从第一次大概几天快速刷完jdbc,到如今的二刷,才发现自己对jdbc的理解有点太浅。到学习javaweb是创建数据库层时的迷茫,到现在对这种设计模式的理解。我深有体会到了:实打实走好每一步的必要性!这篇笔记较为完整的展示了jdbc的发展脉络,从原理到手动封装,再到第三方库,循序渐进。
## jdbc概述
- jdbc为访问不同的数据库提供了统一的接口。
- java程序员使用jdbc,可以连接任何提供了jdbc驱动程序的数据库系统,从而完成对数据库的各种操作
- jdbc的基本原理图
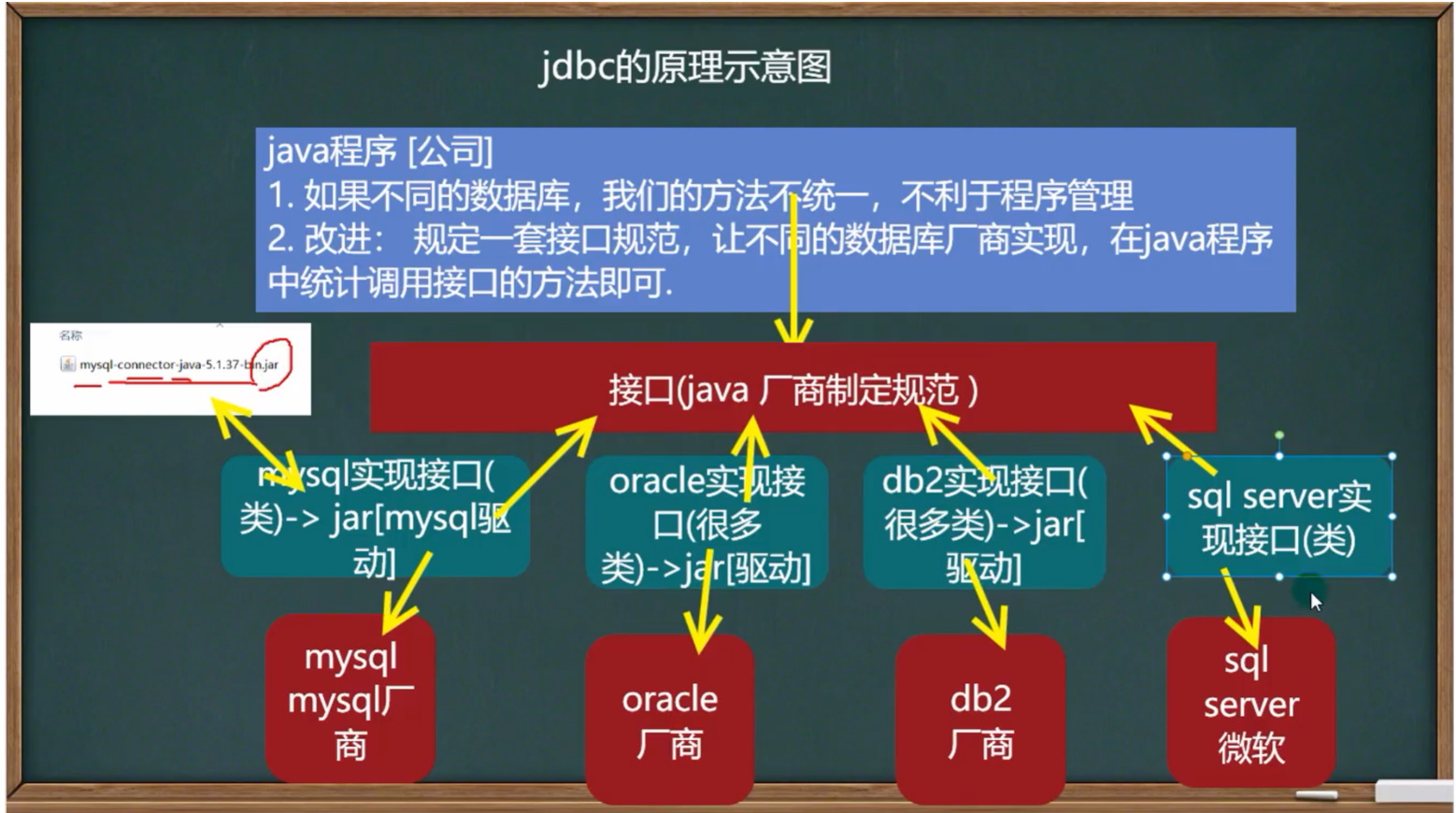
java程序通过制定一些接口,让数据库厂商实现这些接口
*************************模拟************************
//java制定的数据库接口
Interface jdbcInterface{
//连接
public Object getConnection();
//crud
public void crud();
//关闭连接
public void close();
}
//mysql厂商继承接口从而实现这些方法
public class MysqlJdbcImpl implements jdbcInterface{
@Override
public Object getConnetion() {
System.out.println(\"mysql的实现\");
return null;
}
@Override
public void crud() {
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
}
java程序使用
public class testjdbc{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//通过接口来调用实现类[动态绑定]
jdbcInterface mysqlImpl = new mysqlImpl();
//通过接口来调用实现类
mysqlImpl.getConnetion();
mysqlImpl.crud();
mysqlImpl.close();
}
}
通过接口来调用实现类的意义:(思考接口编程的好处)
当用户用其他数据库厂商的实现类时只需动态绑定其他数据库实现类
例如上方:jdbcInterface mysqlImpl = new DB2Impl();
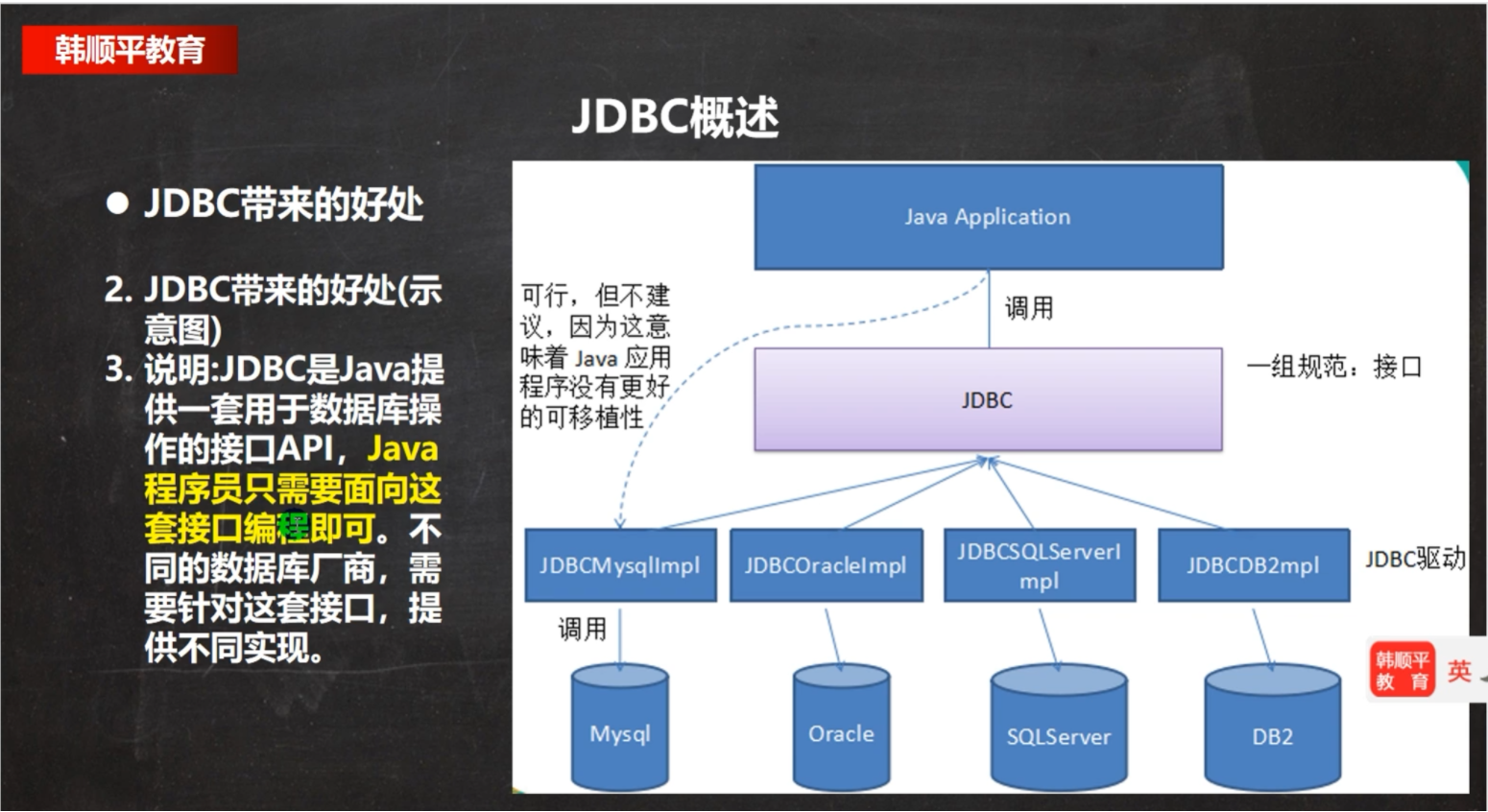

jdbc程序编写步骤
- 注册驱动-加载Driver类
- 获取连接-得到Connection
- 执行增删改查-发送sql给相应的数据库执行
- 释放资源-关闭相关的连接
简单的步骤:
-
导入对应的jar包,即驱动文件
-
注册驱动
Derver driver=new new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
-->简写为 Derver driver=new driver();
-
String url 解读
String url=\"jdbc::mysql://ip:port/数据库名\"
jdbc::mysql://规定好的,表示一个协议,通过jdbc的方式连接mysql。
ip 连接到的主机名称
3306 表示mysql监听的端口
数据库名 表示连接到mysql dbms的哪一个数据库
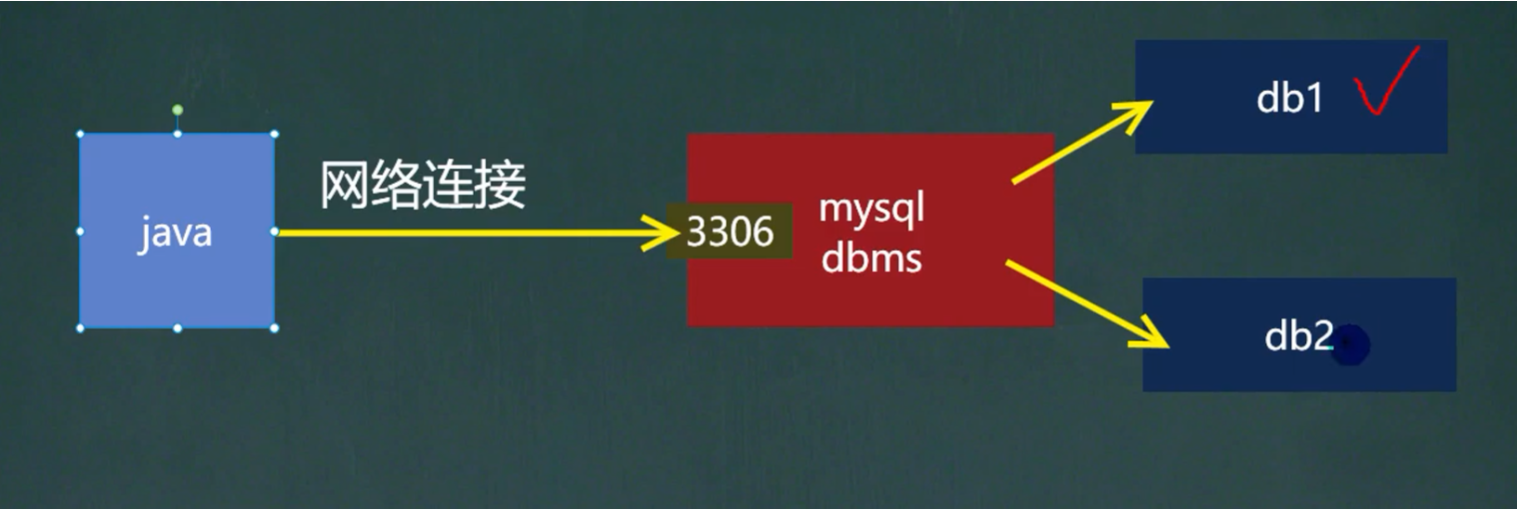
mysql的连接本质就是socket连接
-
将用户名和密码放入到properties对象中
Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.setProperty(\"user\",\"book\");//用户 properties.setProperty(\"password\",\"xxxx\");//密码 -
得到连接
Connection conn=driver.connect(url,properties); -
执行sql
String sql=\"select * from xxx\";Statement用于执行sql语句
Statement statement=conn.createStatement(); int i=statement.excuteUpdate(sql); //i表示受影响的行数 -
关闭资源
statemen.close(); conn.close();不关闭资源造成的影响:会造成连接不到mysql
获取数据库连接的五种方式
1.方式一 获取Driver实现类对象
Driver driver=new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
String url=\"jdbc:mysql://ip:port/数据库名\";
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.setProperty(\"user\",\"name\");
properties.setProperty(\"password\",\"xxxx\");
Connection conn=driver.connect(url,properties);
通过new了一个第三方的driver,第三方的dirver 是静态加载,灵活性不高。
2.方式二 使用反射机制,动态加载。
//使用反射加载Driver类
Class clazz=Class.forName(\"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver\");
Driver driver= (Driver) clazz.newInstance();
String url=\"jdbc:mysql://ip:port/数据库名\";
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.setProperty(\"user\",\"name\");
properties.setProperty(\"password\",\"xxxx\");
Connection conn=driver.connect(url,properties);
反射动态加载,更加灵活,减少依赖性。
3.方式三使用DriverManager进行统一管理
//使用反射加载Driver
Class clazz=Class.forName(\"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver\");
Driver driver= (Driver) clazz.newInstance();
//创建url user password
String url=\"jdbc:mysql://ip:port/数据库名\";
String user=\"root\";
String password=\"xxxx\";
//注册Driver驱动
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
DriverManagaer用于管理一组jdbc驱动程序的基本服务
4.方式四使用forName()自动完成注册驱动,简化代码--推荐使用
//使用反射加载Driver
Class clazz=Class.forName(\"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver\");
//创建url user password
String url=\"jdbc:mysql://ip:port/数据库名\";
String user=\"root\";
String password=\"xxxx\";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
Class.forName 在加载Driver类时自动完成了注册
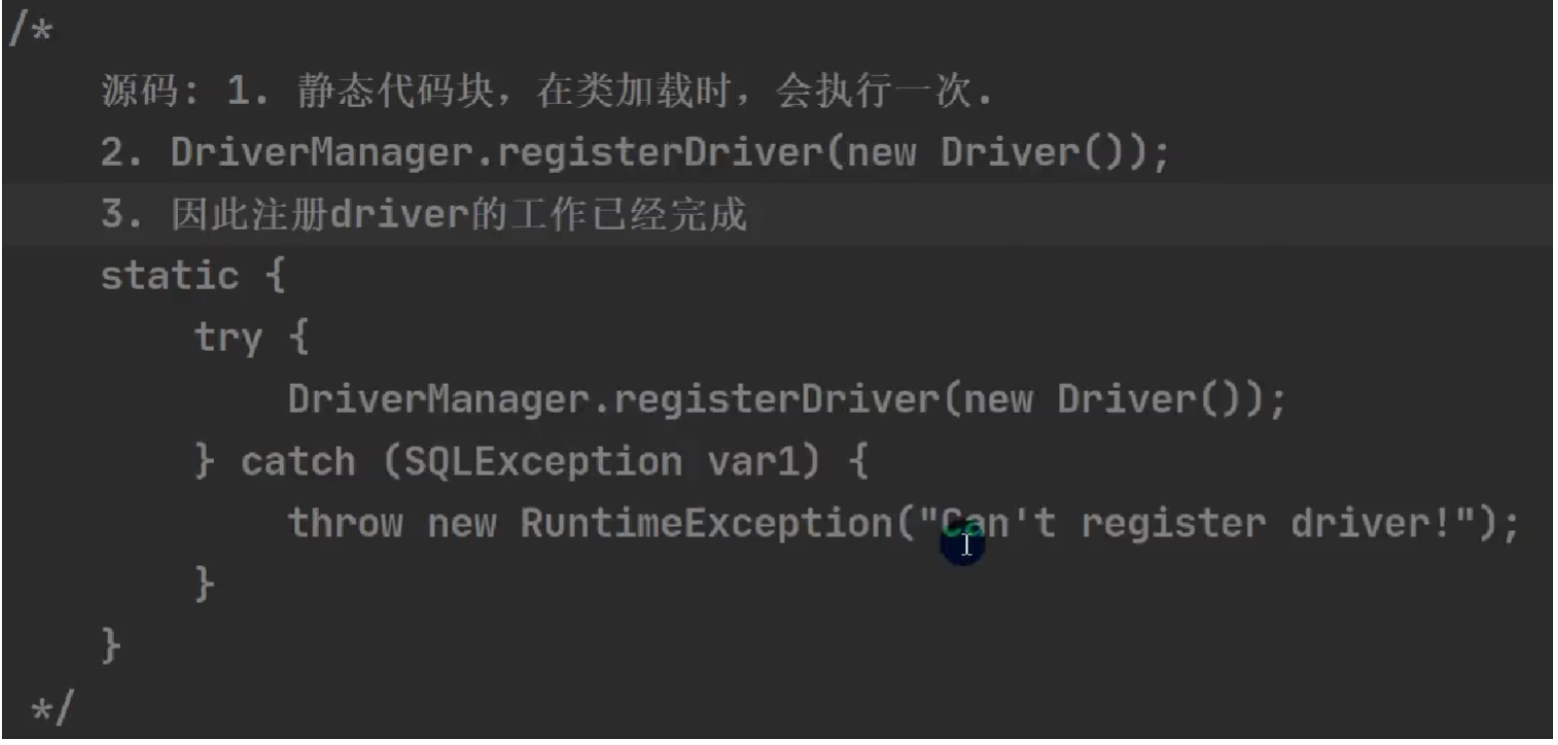
tip:没用显示调用Class.forName(\"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver\")仍然可以拿到数据库的连接。建议写上,更加明确

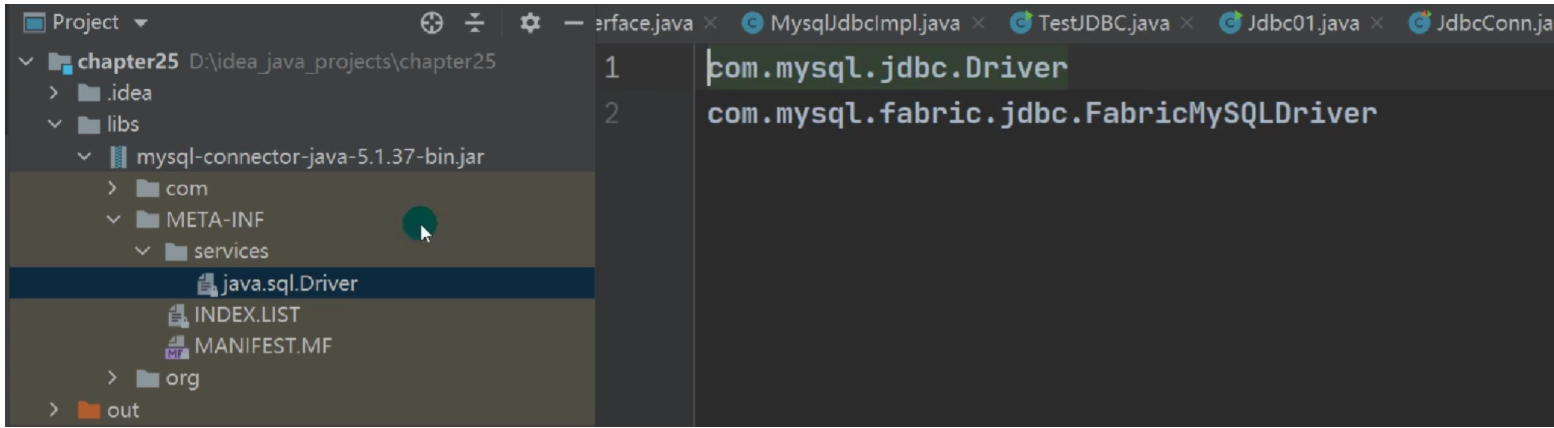
5.方式五通过写配置文件,让连接更加灵活
//通过Peoperties对象获取配置文件的信息
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream(\"com\\\\mysql.properties\"));
//通过key获取相关的值
String user = properties.getProperty(\"user\");
String password = properties.getProperty(\"password\");
String url = properties.getProperty(\"url\");
String driver = properties.getProperty(\"driver\");
Class.forName(driver);
DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
在方式四的基础上,增加配置文件,让连接更加灵活。
配置文件:
#key=value
user=root
password=xxx
url=jdbc:mysql://ip:port/数据库名
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
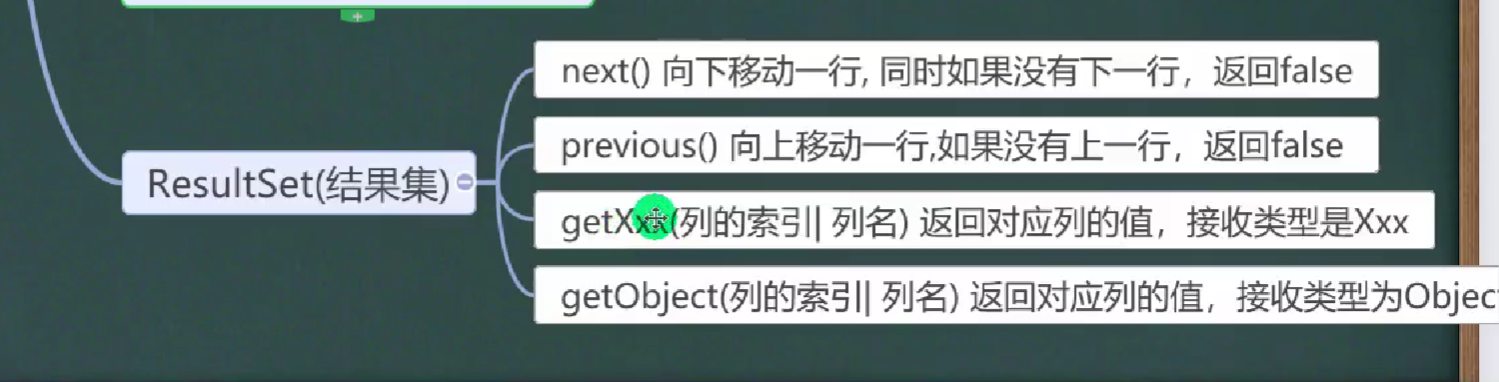
ResultSet结果集--底层(?)
概述:表示数据库结果集的数据表,通常通过查询数据库的语句生成。ResultSet对象保持一个光标指向其当前的数据行,最初光标位于第一行,next方法将光标移动到下一行,并且由于在ResultSet对象中没有更多行时返回false。类似于迭代器。
//得到Statemen
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//sql语句
String sql=\"SELECT * FROM xxx\";
//执行给定的sql语句,该语句返回单个ResultSet对象即为一张表
java.sql.ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
//循环取出
while(resultSet.next()){//让光标向后移动,如果没有更多行,则返回false
resultSet.getInt(1);//获取改行的第一列数据
resultSet.getString(2);//获取该行第二列
}
//关闭资源
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
statement--存在sql注入问题
概述:用于执行静态的sql语句并返回其生成的结果的对象
statement是一个接口需要不同的数据库厂商实现
解决方案:使用preperdStatement
代码实现:
//得到Statemen
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//sql语句xx
String sql=\"SELECT * FROM xxx\";
//执行给定的sql语句,该语句返回单个ResultSet对象即为一张表
java.sql.ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
如果将用户输入改成next()也可以防止sql注入,next遇到空格会停止。
PreperdStatement
概述:预处理Statement,是一个接口。
用法:
1.PreperdStatement执行的sql语句中的参数用问号(?)来表示,调用PreperdStatement对象的setXXX()方法来设置这些参数。setXXX()方法有两个参数,第一个参数是要设置的sql语句中的参数的索引(即第几个问号),第二个设置的是参数的值。
2.调用executeQuery(),返回ResultSet对象
3.调用excuteUpdate(),执行crud。返回影响行数
预处理好处:
不在使用+拼接sql语句,减少语法错误,有效解决了sql注入问题,减少了编译次数,效率较高。
预处理就是再执行sql之前就已经完成对sql的赋值。
代码实现:
//sql语句xx,设置问号
String sql=\"SELECT * FROM xxx WHERE name=?and password=?\";
//得到PreparedStatemen
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//给问号赋值
preparedStatement.setString(1,user_name);
preparedStatement.setString(2,user_pass);
//执行注意执行的时候不需要再填sql
preparedStatement.executeQuery();
添加记录dml
String sql=\"INSERT INTO xxx VALUES(?,?)\";
API小结
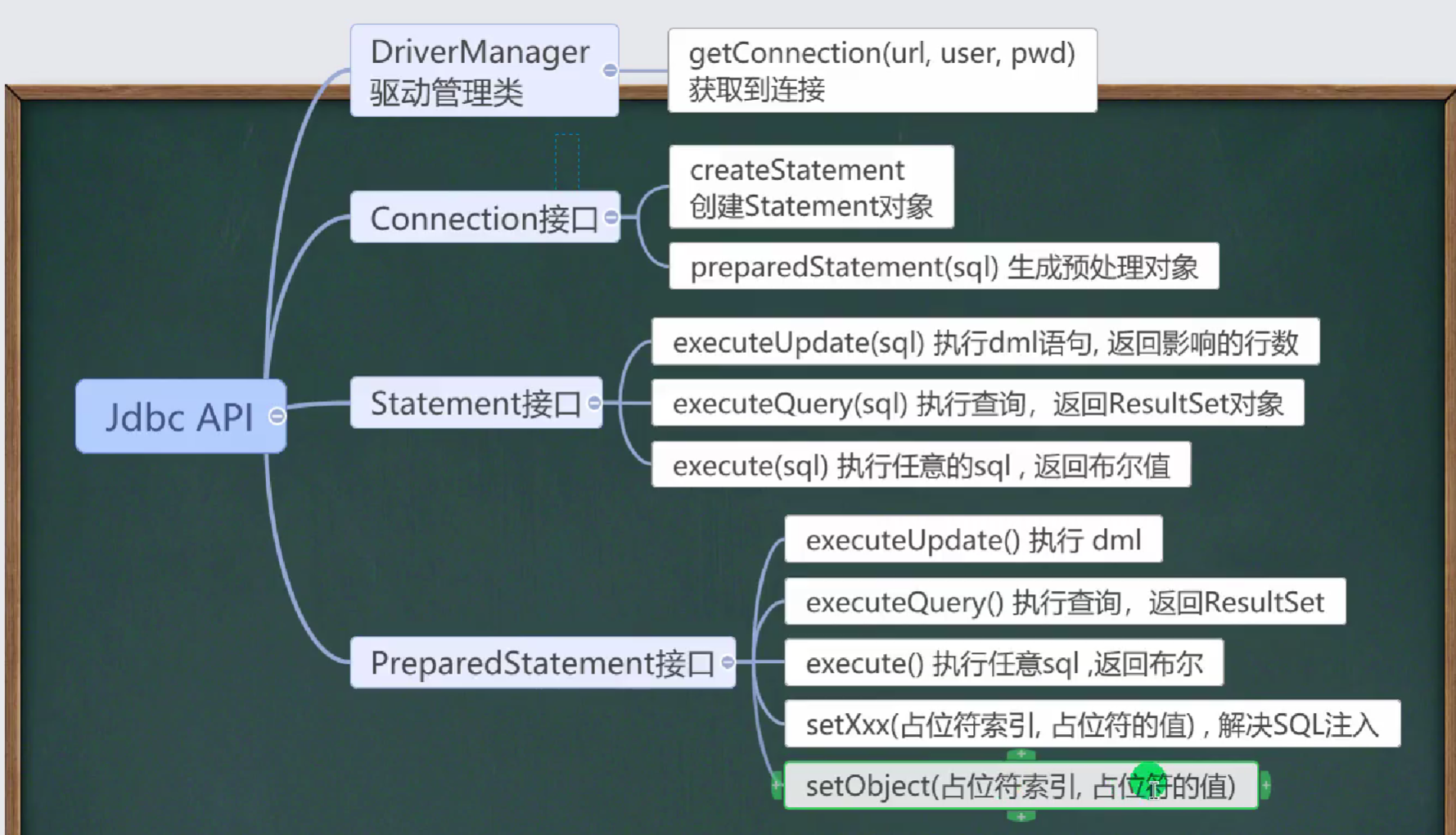
封装Utils类
简介:在jdbc操作中,获取数据库连接和释放资源是经常使用到的可以将其封装为JDBC连接的工具类Utils。
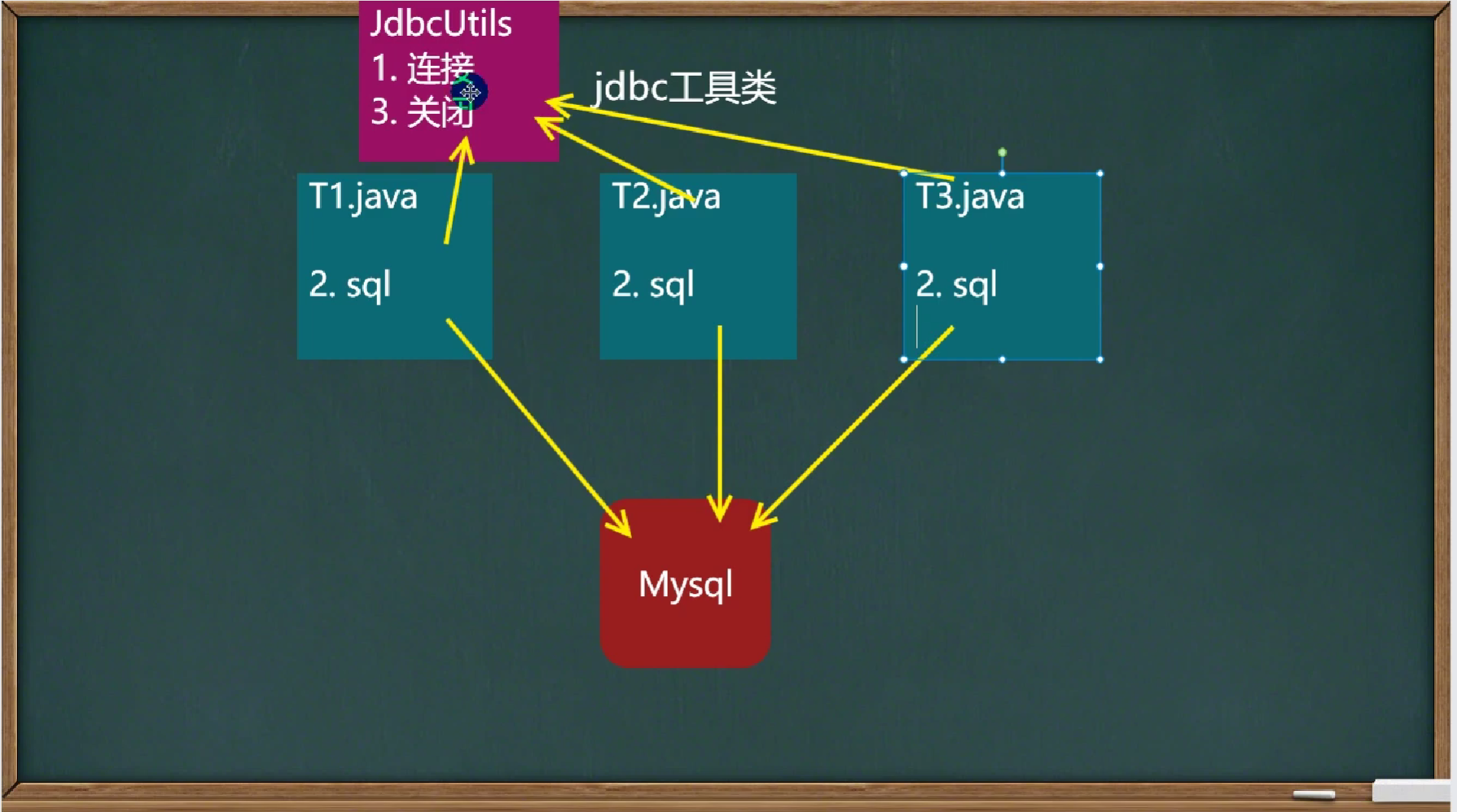
使用步骤:
- 定义相关的属性(4个),因为只需要一份,所以用static修饰
- 在static代码块初始化
- 通过配置文件读取相关的属性值
- 写连接函数,推荐使用DriverManager
- 写释放资源函数
代码实现:
//定义相关的属性(4个),因为只需要一份,所以用static修饰
private static String user;//用户名
private static String password;//密码
private static String url;//数据库url
private static String driver;//驱动名
//在static代码块初始化
static{
try {
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream(\"com\\\\mysql.properties\"));
//读取相关的属性值
user = properties.getProperty(\"user\");
password=properties.getProperty(\"password\");
url=properties.getProperty(\"url\");
driver=properties.getProperty(\"driver\");
} catch (IOException e) {
//在实际开发中,常常转为运行异常抛出
//将编译异常转为运行异常,调用者可以选择捕获该异常,也可以选择默认处理该异常,比较方便。
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//连接数据库,返回Connection
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
Class.forName(driver);
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
}
//关闭相应资源
/*
可能关闭的资源
1.ResultSet结果集
2.Statement和preparedStatement
3.connection
4.如果需要关闭资源,则传入对象,否则传入null
*/
//用statement来接受因为statement是preparedStatement的父接口,都可以接收
/*
当一个对象被当作参数传递到一个方法后,此方法可改变这个对象的属性,并可返回变化后的结果,那么这里到底是值传递还是引用传递?
Java 编程语言只有值传递参数。当一个对象实例作为一个参数被传递到方法中时,参数的值就是对该对象的引用。对象的内容可以在被调用的方法中改变,但对象的引用是永远不会改变的。
*/
public static void close(ResultSet resultSet, Statement state,Connection conn) throws SQLException {
if(resultSet!=null){
resultSet.close();
}
if(state!=null){
state.close();
}
if(conn!=null){
state.close();
}
}
实际开发过程中异常处理:
在实际开发中,常常转为运行异常抛出,将编译异常转为运行异常,调用者可以选择捕获该异常,也可以选择默认处理该异常,比较方便。throw new RuntimeException(e);
Java是值传递:
Java 编程语言只有值传递参数。当一个对象实例作为一个参数被传递到方法中时,参数的值就是对该对象的引用。对象的内容可以在被调用的方法中改变,但对象的引用是永远不会改变的。
Utils使用
使用步骤:
- 得到连接。
- 组织一个sql语句。
- 创建一个PreparedStatement对象。
- 执行sql语句。
- 释放资源调用close()。
代码实现:
public class use_utils {
public void use_ut() throws SQLException {
Connection conn=null;
String sql=\"SELECT * FROM xxx\";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
try {
//得到连接
conn=jdbcutils.getConnection();
//创建PreparedStaement
preparedStatement= conn.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeQuery();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcutils.close(null,preparedStatement,conn);
}
}
}
事务
概述:Jdbc程序中当一个Connection对象创建时,默认情况下是自动提交事务,不能回滚。并且jdbc程序中为了让多个SQL语句作为一个整体执行,需要使用事务,调用Connection的setAutoCommit(false)可以取消自动提交事务,当所有的sql语句都执行后,调用Commit()方法即可提交事务,在其中某个操作失败或出现异常时,调用rollback()方法即可回滚事务。
默认情况下,Connection对象是自动提交的。
应用实例:经典的转账业务。
代码实现: \"未使用事务\"
Connection conn=null;
String sql=\"update account set balance=balance-100 where id=1\";
String sql2=\"update account set balance=balance+100 where id=2\";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
try {
//得到连接
conn=jdbcutils.getConnection();
//创建PreparedStaement
preparedStatement= conn.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeQuery();//执行第一条sql
int i=1/0;//抛出异常
preparedStatement=conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
preparedStatement.executeQuery();//执行第二条SQL
}
上述代码,在执行sql时如果没用开启事务,会造成第一条sql执行成功,而第二条sql未执行便被捕获异常,在转账问题方面就会出现问题。
代码实现: 开启事务
//得到连接
conn=jdbcutils.getConnection() //创建PreparedStaement
preparedStatement= conn.prepareStatement(sql);
/*得到连接后将conn设置为不自动提交*/
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
preparedStatement.executeQuery();//执行第一条sql
int i=1/0;//抛出异常
preparedStatement=conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
preparedStatement.executeQuery();//执行第二条SQL
/*在catch中即可处理异常,撤消先前已经执行的sql*/
/*即回滚*/
catch(Exception e){
conn.rollback();
}
rollback默认回滚到事务开启的地方。
批处理
概述:当需要成批插入或者更新数据时,可以采用Java批量更新机制,这一机制允许将多条语句一次性提交给数据库批量处理。
批处理步骤:
-
如果使用批处理时,需要在url中添加参数:
?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
-
addBatch():添加需要批量处理的SQL语句或参数
-
excuteBatch():执行批量处理的语句
-
clearBatch():清空批处理包的语句
批处理优势:批处理往往和PreparedStatement一起搭配使用,既可以减少编译次数,又减少运行次数,让效率提高。
代码实现:
传统代码
public void nobatch() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
Connection connection = jdbcutils.getConnection();
String sql=\"insert into xxx values(null,?,?)\";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1,\"tom\"+i);
preparedStatement.setString(2,\"xxx\");
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}
//关闭连接
jdbcutils.close(null,preparedStatement,connection);
}
批处理代码
public void batch_() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
Connection connection = jdbcutils.getConnection();
String sql=\"insert into xxx values(null,?,?)\";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1,\"tom\"+i);
preparedStatement.setString(2,\"xxx\");
/*preparedStatement.executeUpdate();*/
//将sql语句加入到批处理包中 ->
preparedStatement.addBatch();
//当有1000条数据时,在批量执行
if((i+1)%1000==0){
//满1000条
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
//清空
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
}
//关闭连接
jdbcutils.close(null,preparedStatement,connection);
}
关键代码:
preparedStatement.addBatch();
//当有1000条数据时,在批量执行
if((i+1)%1000==0){
//满1000条
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
//清空
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
注:源代码未了解!
数据库连接池
概述:传统方式连接数据库过多,由于没用的连接资源未被及时断开会造成,连接不上数s据库,数据库连接池就诞生了,数据库连接池可以合理分配连接资源。
实现方式:
1.预先在缓冲池中放入一定数量的连接,当需要建立数据库连接时,只需要从 \"缓冲池\"中取出一个,使用完毕之后再放回去。
2.数据库连接池负责分配,管理和释放数据库连接,它允许应用程序重复使用一个现有的数据库连接,而不是重写建立一个
3.当应用程序向连接池请求的连接数超过最大连接数量时,这些请求将被加入到等待队列中。
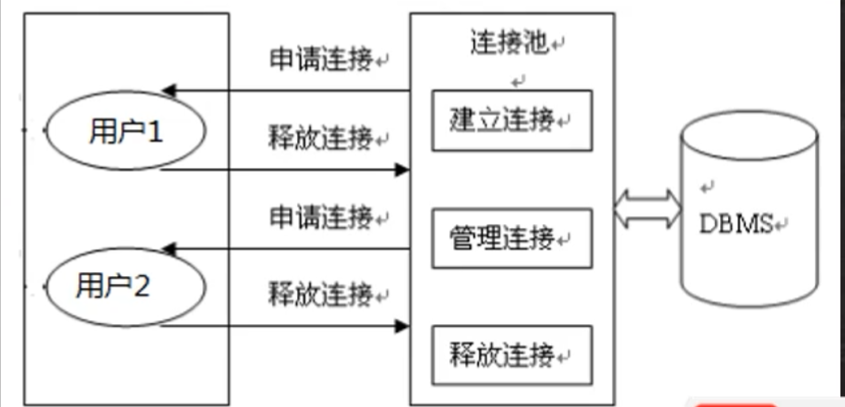

数据库连接池种类:
1.Jdbc的数据库连接池使用java.sql.dateSource来表示,DateSource只是一个接口,该接口由第三方提供实现。
2.C3P0, DBCP, Proxool, BoneCP, Druid
C3P0
实现步骤:
一、传统方式
1.创建一个数据源对象。
2.通过配置文件获取相关的信息user,url...
3.给数据源ComboPooledDataSource(c3p0)设置相关的参数url,user...setInitialPoolSize()方法设置初始化连接数,setMaxPoolSize()方法设置最大连接数。
4.得到连接。
5.关闭连接--即放回到连接池中。
二、使用配置文件模板
概述:c3p0设计者提供了一个xml文件,方便配置
1.将C3P0提供的配置文件 c3p0.config.xml拷贝到src目录下
2.创建一个数据源对象,参数即为c3p0.config.xml文件中的
3.得到连接
4.关闭连接--即放回到连接池中。
C3P0:
配置文件:c3p0.config.xml
<c3p0-config>
<!-- 数据源名称代表连接池-->
<name-config name=\"xxx\">
<!-- 连接参数 -->
<property name=\"driverClass\">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name=\"jdbcUrl\">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/web</property>
<property name=\"user\">root</property>
<property name=\"password\">ROOT</property>
<!-- 连接池参数 -->
<!-- 每次增长连接池可供连接数 -->
<property name=\"acquireIncrement\">10</property>
<!-- 初始连接数 -->
<property name=\"initialPoolSize\">5</property>
<!-- 最大连接数 -->
<property name=\"maxPoolSize\">10</property>
<!-- 最大等待时间 -->
<property name=\"checkoutTimeout\">2000</property>
<!-- 最大空闲回收时间 -->
<property name=\"maxIdleTime\">1000</property>
</c3p0-config>
代码实现:
传统方式
public void testc3p0() throws IOException, PropertyVetoException, SQLException {
//1.创建一个数据源对象
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
//2.通过配置文件获取相关的信息
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream(\"com\\\\mysql.properties\"));
String user = properties.getProperty(\"user\");
String password = properties.getProperty(\"password\");
String url = properties.getProperty(\"url\");
String driver = properties.getProperty(\"driver\");
//给数据源 comboPooledDataSource设置相关的参数。
//我们连接的管理是由comboPooledDataSource来管理的。
comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(driver);
comboPooledDataSource.setUser(user);
comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(password);
comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl(url);
//设置连接数--初始化连接数
comboPooledDataSource.setInitialPoolSize(10);
//最大连接数
comboPooledDataSource.setMaxPoolSize(50);
Connection connection = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();//这个方法就是从DateSource接口实现的
connection.close();
}
xml配置文件的方式
public void test04() throws SQLException {
//1.将配置文件导入src目录下
//2.创建一个数据源对象,参数即为c3p0.config.xml文件中的 <name-config name=\"nihao\">
////数据源会根据数据源名称读取xml文件中的内容
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(\"nihao\");
Connection connection = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();
connection.close();
}
注:数据源名称不能写错,并且xml文件的名称是固定的,数据源会根据数据源名称读取xml文件中的内容,自动完成配置。
Druid
概述:
Druid连接池是阿里实现的,获取连接的速度比较快。
实现步骤:
1.添加jar包,和properties配置文件,将配置文件拷贝到项目的src目录下。
driverClassName 底层用这个字段来读取数据库驱动。
minIdle 空闲时候的连接数量
2.创建Properties对象来读取配置文件
3.创建一个指定参数的数据库连接池
4.得到连接
5.释放连接
代码实现:
public void druidx() throws Exception {
/*
1.添加jar包,和properties配置文件,将配置文件拷贝到项目的src目录下。
driverClassName 底层用这个字段来读取数据库驱动。
minIdle 空闲时候的连接数量
2.创建Properties对象来读取配置文件
*/
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream(\"src\\\\druid.properties\"));
//创建一个指定参数的数据库连接池
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
//得到连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
connection.close();
}
配置文件: druid.properties
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver //驱动加载
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/student?characterEncoding=utf-8 //注册驱动
username=root //连接数据库的用户名
password=sjw58586 //连接数据库的密码。
filters=stat //属性类型的字符串,通过别名的方式配置扩展插件, 监控统计用的stat 日志用log4j 防御sql注入:wall
initialSize=2 //初始化时池中建立的物理连接个数。
maxActive=300 //最大的可活跃的连接池数量
maxWait=60000 //获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒,超过连接就会失效。配置了maxWait之后,缺省启用公平锁,并发效率会有所下降, 如果需要可以通过配置useUnfairLock属性为true使用非公平锁。
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=60000 // 连接回收器的运行周期时间,时间到了清理池中空闲的连接,testWhileIdle根据这个判断
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis=300000
validationQuery=SELECT 1 //用来检测连接是否有效的sql,要求是一个查询语句。
testWhileIdle=true //建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性。 申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis, 执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。
testOnBorrow=false //申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能。设置为false
testOnReturn=false //归还连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能,设置为flase
poolPreparedStatements=false //是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache。
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize=200 // 池中能够缓冲的preparedStatements语句数量
将Jdbc工具类改成druid实现
代码实现:
private static DataSource ds;
//在静态代码块完成ds初始化
static{
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream(\"src\\\\druid.properties\"));
ds= DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//得到连接方法
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return ds.getConnection();
}
//释放资源,Connection放回连接池,此是的close是数据库连接池实现的close方法。
public void close(ResultSet rs, Connection conn, Statement st) throws SQLException {
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
if (conn!=null){
conn.close();
}
if(st!=null){
st.close();
}
}
注:此时调用的close方法,是连接池实现的close()方法并不会真正的关闭连接,而是将连接放回到数据库连接池。
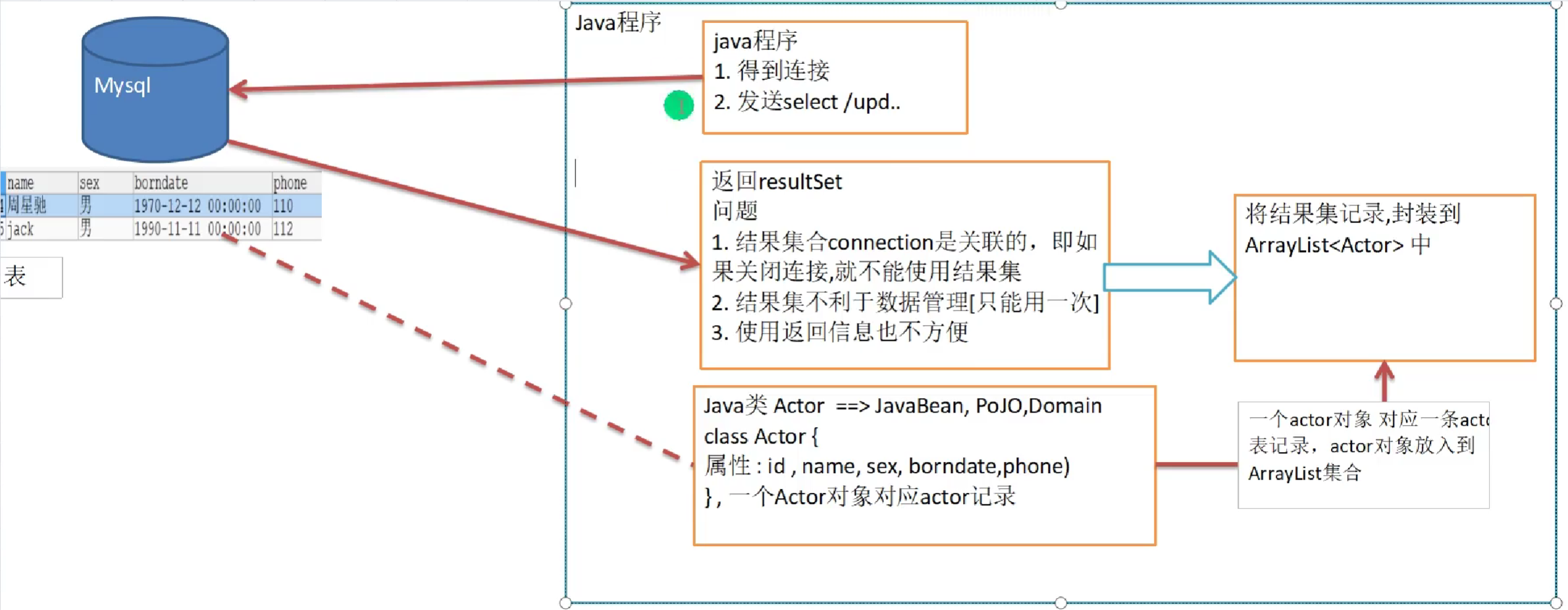
Bean,Domain,POJO
问题引出:
1.java程序使用Connection连接,Connection和ResultSet关联,当关闭Connection无法再使用ResultSet。
2.如果一个程序返回ResultSet对象,这是已经关闭Connection,仍然无法拿到结果集对象,导致结果集只能使用一次。
解决方案:
写一个Java类---->常被叫做Bean,Domain,POJO,该类中有查询到的表中的字段属性,让一个Actor对象对应查询到的一条记录,将结果集封装到ArrayList中。
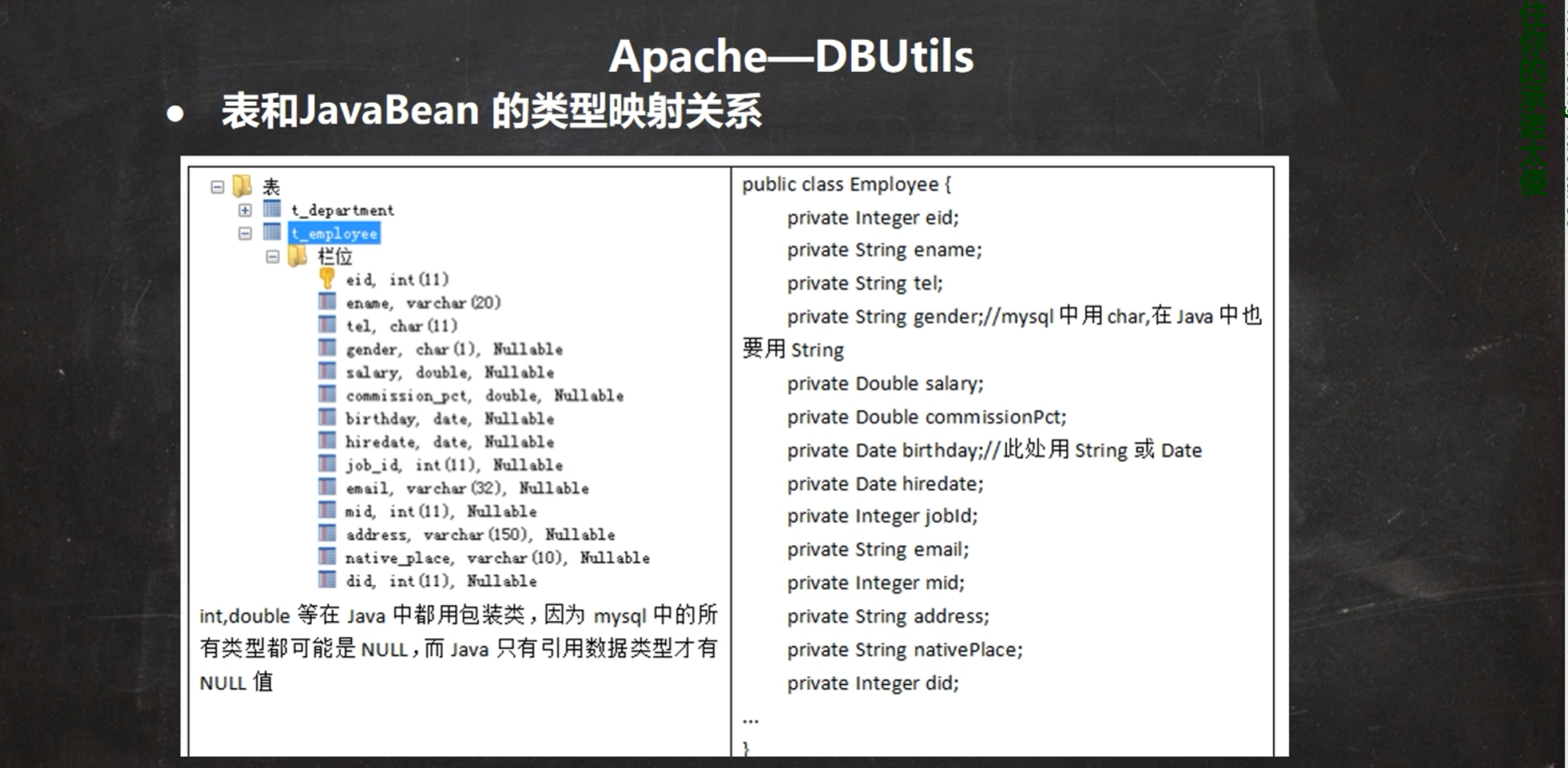
ApachDBUtils
概述:面对ResultSet问题,ApachDBUtils工具类完美解决了这个问题。
传统方式解决(土方法封装)
实现步骤:
1.新建一个POJO类,用于封装查询到的表的记录。
2.类中定义表中相对应的字段,构造函数,setter,getter方法。
注:一定要给一个默认构造函数[反射需要]。
3.在java程序中用ArrayList 来存贮数据。
4.在ResultSet遍历的时候,封装数据,存储到集合中。
代码实现:
Actor---POJO
import java.util.Date;
public class Actor {//POJO
//和表的字段相对应
//细节建议用Integer装箱
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String sex;
//Date用util包下的。
private Date bornDate;
private String phone;
//一定要给一个无参构造器[反射会需要]
public Actor(){
}
public Actor(Integer id, String name, String sex, Date bornDate, String phone) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.bornDate = bornDate;
this.phone = phone;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public void setBornDate(Date bornDate) {
this.bornDate = bornDate;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public Date getBornDate() {
return bornDate;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
}
java程序:
public void testSelecttoArraylist() throws Exception {
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream(\"com\\\\mysql.properties\"));
//通过key获取相关的值
String user_name;
String user_pass;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
user_name=scanner.nextLine();
user_pass=scanner.nextLine();
String user = properties.getProperty(\"user\");
String password = properties.getProperty(\"password\");
String url = properties.getProperty(\"url\");
String driver = properties.getProperty(\"driver\");
//创建ArrayList对象,存放Actor对象
ArrayList<Actor> list=new ArrayList<>();
//注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//得到连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//sql语句xx,设置问号
String sql=\"SELECT * FROM xxx WHERE name=?and password=?\";
//得到PreparedStatemen
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//给问号赋值
preparedStatement.setString(1,user_name);
preparedStatement.setString(2,user_pass);
//执行给定的sql语句,该语句返回单个ResultSet对象即为一张表
java.sql.ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(sql);
//循环取出
while(resultSet.next()){//让光标向后移动,如果没有更多行,则返回false
int id=resultSet.getInt(\"id\");
String name = resultSet.getString(\"name\");
String sex = resultSet.getString(\"sex\");
Date borndate = resultSet.getDate(\"borndate\");
String phone = resultSet.getString(\"phone\");
//把得到的resultSet记录封装到Actor对象,放入到list集合。
list.add(new Actor(id,name,sex,borndate,phone));
}
//关闭资源
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
ApachDBUtils解决
概述:commons-dbutils是Apache组织提供的一个开源的JDBC工具类库,它是对JDBC的封装,使用dbutils能极大简化jdbc编码的工作量。
dbutils常用类和接口:
- QueryRunner类:该类封装了SQl的执行,是线程安全的,可以实现增删改查,批处理。
- ResultSetHandler接口:该接口用于处理java.sql.ResultSet,将数据按要求转换为另一种形式。
ArrayHandler: 把结果集中的第一行数据转成对象数组
ArrayListHandler: 把结果集中的每一行数据都转成一个数组,再存放到List中。
BeanHandler: 将结果集中的第一行数据封装到一个对应的JavaBean实例中。
BeanListHandler: 将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个对应的JavaBean: 实例中,存放到List里。
ColumnListHandler: 将结果集中某一列的数据存放到List中。
KeyedHandler(name): 将结果集中的每行数据都封装到Map里,再把这些map再存到一个map里,其key为指定的key。
MapHandler: 将结果集中的第一行数据封装到一个Map里,key是列名,vaue就是对应的值。
MapListHandler: 将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个Map里,然后再存放到List
使用步骤:druid+dbutils
-
引入commons jar包
-
使用自己封装的DruidUtils得到连接
-
创建QueryRunner
-
调用QueryRunner的query方法执行sql返回ArrayList集合
注:sql语句也可以查询部分列
BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class):在将ResultSet->Actor 对象->封装到ArrayList
1: 传给sql中的问号的,可以有多个后边是可变参数Object...params
底层得到的ResultSet会在query执行后关闭,PreparedStatement也会自动关闭
参数列表 (connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class), 1) -
关闭连接。
代码实现:
public void querytest() throws SQLException {
//得到连接(druid)
Connection connection = DruidUtils.getConnection();
//使用DbUtils类和接口,引入相应的jar文件。
//创建QueryRunner
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//QueryRunner就可以执行相关的方法,返回ArrayList结果集
String sql=\"SELECT * FROM xxx WHERE id>=?\";
//sql语句也可以查询部分列
/*
queryRunner.query方法就是执行一个sql语句得到ResultSet,--封装到ArrayList集合中
然后返回集合。
参数Connection 连接
sql: 执行的sql语句
BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class):在将ResultSet->Actor 对象->封装到ArrayList
底层使用反射机制获取Actor属性进行封装
1: 传给sql中的问号的,可以有多个后边是可变参数Object...params
底层得到的ResultSet会在query执行后关闭,PreparedStatement也会自动关闭
* */
List<Actor> list = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class), 1);
DruidUtils.close(null,connection,null);
}
dbutils查询单行记录(单个对象)
解决方案:返回单行记录,单个对象使用的Hander是BeanHandler
new BeanHandler<>(Actor.class)
单行单列:返回的是一个Object,对象使用Handers是ScalarHandler()
new ScalarHandler()
dbutils+druid实现crud
执行dml操作使用queryRunner.update()
返回值是受影响的行数。
代码实现:
public void testcrud() throws Exception{
Connection connection = DruidUtils.getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql=\"update actor set name=? where id=?\";
int affectedrows = queryRunner.update(connection, sql, \"niuma\", 4);
}
对应关系:
注: java中全部对应包装类。
BasicDAO
问题分析:
dbutils和druid简化了JDBC开发,但有不足
1.Sql语句是固定,不能通过参数传入,通用性不好,需要进行该进,更方便执行crud
2.对于select操作,如果有返回值,返回值类型不能固定,需要使用泛型
3.将来的表很多,业务需求复杂,不可能只靠一个Java类完成
设计理念:各司其职。一张表对应一个DAO
DAO:访问数据的对象
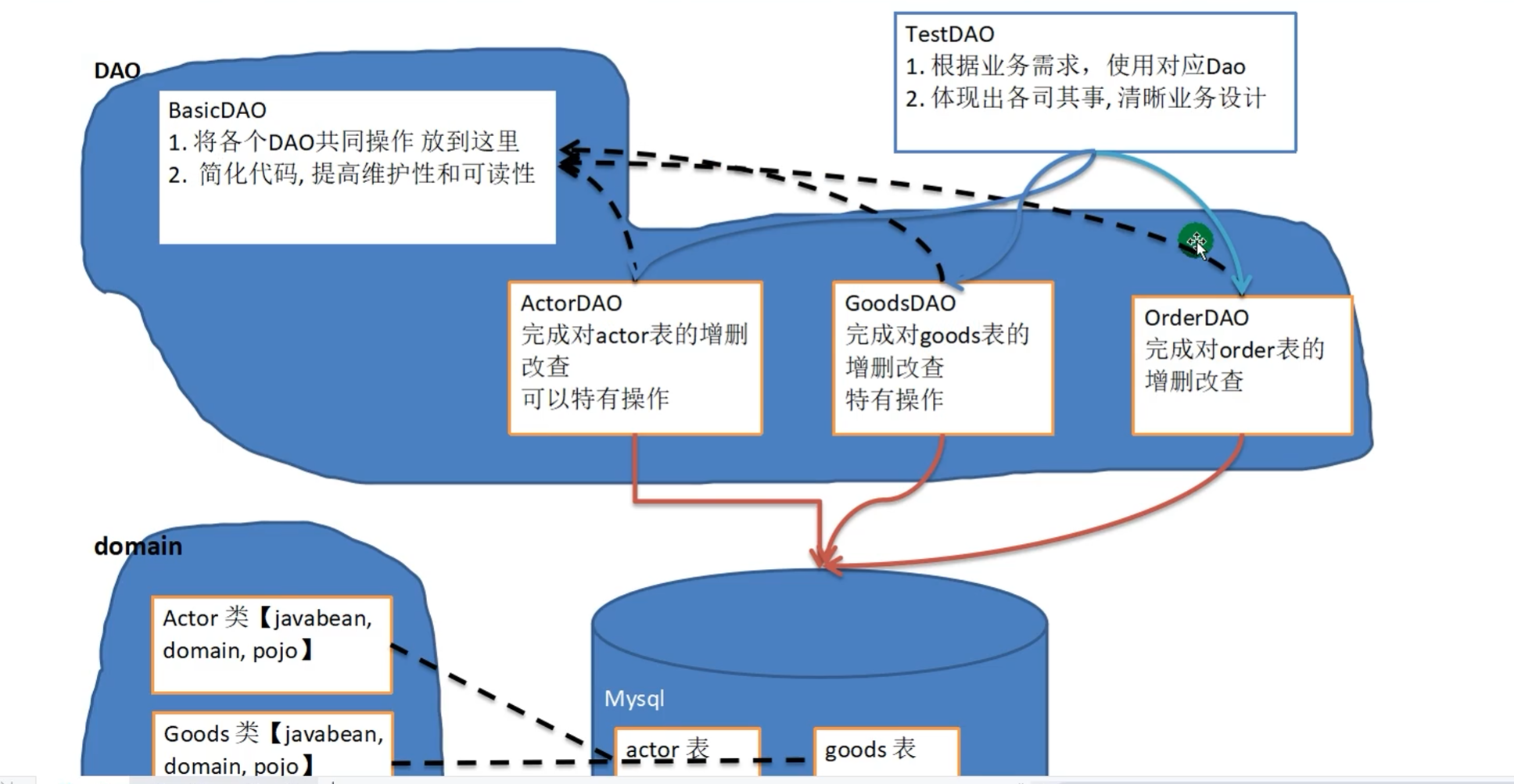
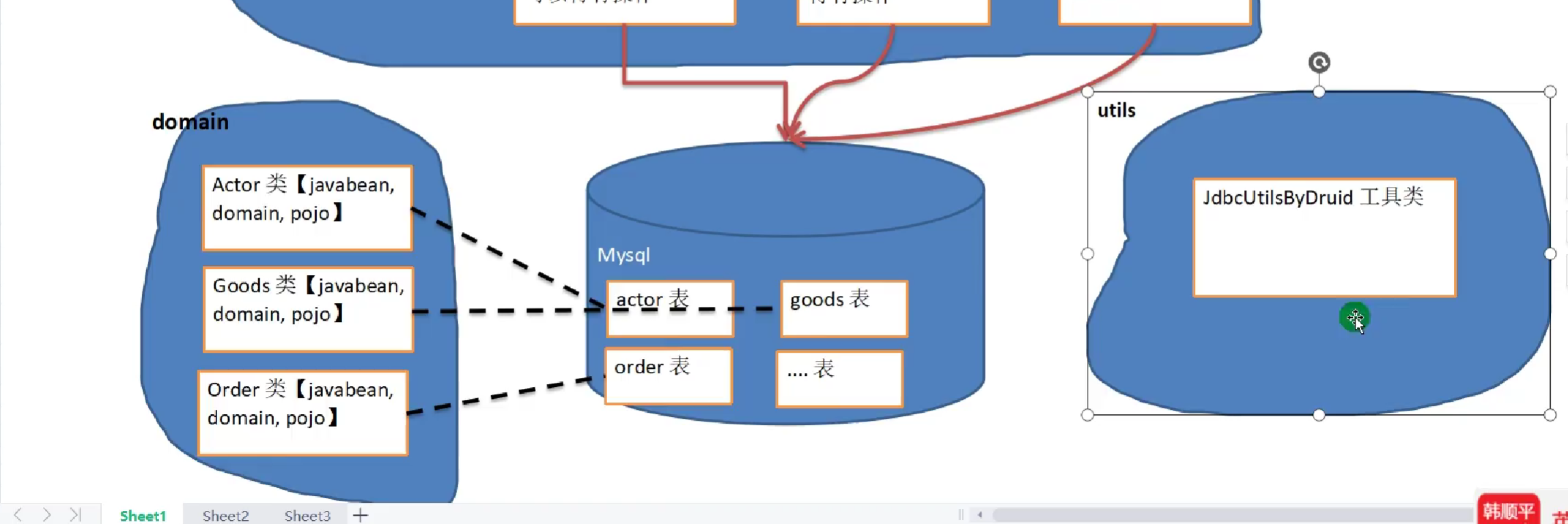
BasicDAO将所有的DAO共有的部分提取出来,让子类去继承简化代码。
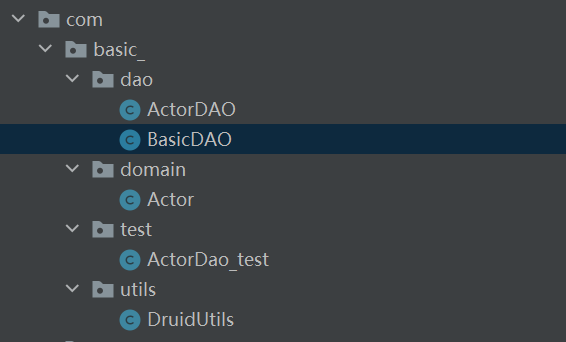
设计步骤:
1.第一个包 放utils工具类
2.第二个包 javaBean/domain
3.第三个包 放xxxDAO和BasicDAO
4.第四个包 写测试类
目录结构:
代码:
BasicDAO:
package com.basic_.dao;
import com.basic_.utils.DruidUtils;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.ScalarHandler;
import javax.management.Query;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
//开发basicDAO
//添加泛型将来是操作domain的
public class BasicDAO<T> {
private QueryRunner qr=new QueryRunner();
//开发通用的dml方法,针对任意的表
public int update(String sql,Object...prameters) throws SQLException {
Connection conn=null;
conn= DruidUtils.getConnection();
int affectedRows = qr.update(conn, sql, prameters);
return affectedRows;
}
//返回多个对象(即查询的结果是多行的),针对任意表
//sql语句可以有问号,占位符
//clazz传入一个类的Class对象,底层通过反射实现domain 比如Actor.class
//prameters传入问号具体的值。
public List<T> queryMulti(String sql, Class<T> clazz, Object...prameters) throws SQLException {
Connection conn=null;
conn=DruidUtils.getConnection();
List<T> list = qr.query(conn, sql, new BeanListHandler<>(clazz), prameters);
DruidUtils.close(null,conn,null);
return list;
}
//查询单行结果通用方法 T可能是Actor..不同的表。
public T querySingle(String sql,Class<T> clazz,Object...prameters) throws SQLException {
Connection conn=null;
conn= DruidUtils.getConnection();
T rs = qr.query(conn, sql, new BeanHandler<>(clazz), prameters);
DruidUtils.close(null,conn,null);
return rs;
}
//查询单行单列即返回单值的方法
public Object queryScalar(String sql,Object...prameters) throws SQLException {
Connection conn=null;
conn= DruidUtils.getConnection();
Object rs = qr.query(conn, sql, new ScalarHandler(), prameters);
DruidUtils.close(null,conn,null);
return rs;
}
}
ActorDAO
public class ActorDAO extends BasicDAO<Actor>{
//Actor有BasicDAO 的方法
//根据业务需求,可以编写特有的方法
}
domain
public class Actor {//POJO
//和表的字段相对应
//细节建议用Integer装箱
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String sex;
//Date用util包下的。
private Date bornDate;
private String phone;
//一定要给一个无参构造器[反射会需要]
public Actor(){
}
public Actor(Integer id, String name, String sex, Date bornDate, String phone) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.bornDate = bornDate;
this.phone = phone;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public void setBornDate(Date bornDate) {
this.bornDate = bornDate;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public Date getBornDate() {
return bornDate;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
}
utils
private static DataSource ds;
//在静态代码块完成ds初始化
static{
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream(\"src\\\\druid.properties\"));
ds= DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//得到连接方法
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return ds.getConnection();
}
//释放资源,Connection放回连接池,此是的close是数据库连接池实现的close方法。
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Connection conn, Statement st) throws SQLException {
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
if (conn!=null){
conn.close();
}
if(st!=null){
st.close();
}
}
测试使用
//测试ActorDao对actor表crud操作
public void testActorDao() throws SQLException {
ActorDAO actorDAO = new ActorDAO();
//1.查询
List<Actor> actors = actorDAO.queryMulti(\"select *from actor where id>?\", Actor.class, 1);
//2.查询单行
Actor actor01 = actorDAO.querySingle(\"select *from actor where id=?\", Actor.class, 1);
//3.查询单行单列
Object o = actorDAO.queryScalar(\"select name from actor where id=?\", 6);
//4.dml操作
//添加数据是按照什么顺序呢?
int afftedRows = actorDAO.update(\"insert into actor values(null,?,?)\", \"nihao\", \"niuma\");
}
作者:程序员包子,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/coder-baozi/p/16290759.html
coder-baozi一位菜鸟码农
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/coder-baozi/p/16290759.html
本站部分图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园
