runAsync 和 supplyAsync
runAsync接受一个Runable的实现,无返回值
CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->System.out.println(\"无返回结果的运行\"));supplyAsync接受一个Supplier的实现,有返回值
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(\"有返回结果的运行\");
return 1;
});获取结果的get和join
都是堵塞,直到返回结果
get方法抛出是经过处理的异常,ExecutionException或**InterruptedException **,需要用户手动捕获
try {
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(\"有返回结果的运行\");
return 1;
}).get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}join方法抛出的就不用捕获,是经过包装的**CompletionException **或 CancellationException
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(\"有返回结果的运行\");
return 1;
}).join());
常用方法
获取结果的get\\join\\getNow
get():一直等待
get(timeout,unit):等待,除非超时
getNow(valueIfAbsent):计算完返回计算的结果,未计算完返回默认的结果
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
});
System.out.println(\"立即获取:\"+completableFuture.getNow(9999));
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(\"doing\");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(\"等一会获取:\"+completableFuture.getNow(9999));join() 同get()
thenApply\\handle
执行完前面的,前面返回的结果返回,然后传给后面再,执行完后面任务,一步一步来。
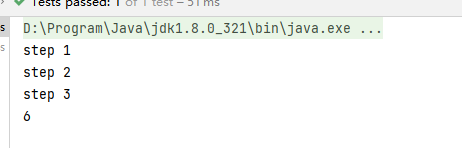
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(\"step 1\");
return 1;
}).thenApply(a -> {
System.out.println(\"step 2\");
return a + 2;
}).thenApply(a -> {
System.out.println(\"step 3\");
return a + 3;
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());执行结果:
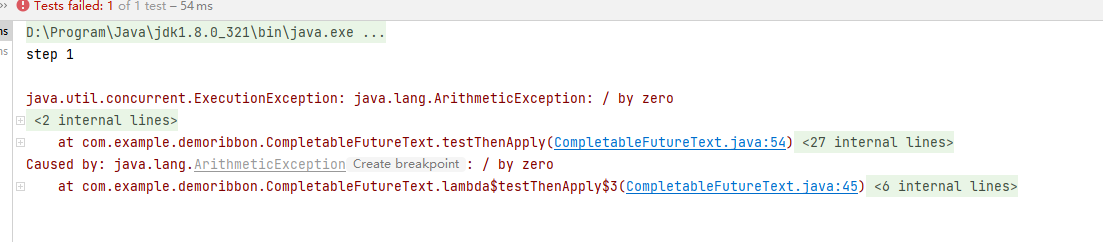
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(\"step 1\");
int a=1/0;
return 1;
}).handle((a,b) -> {
System.out.println(\"step 2\");
if (b!=null) {
System.out.println(b.getMessage());
return 0;
}
return a + 2;
}).handle((a,b) -> {
System.out.println(\"step 3\");
if (b!=null) {
System.out.println(b.getMessage());
return 0;
}
return a + 3;
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());执行结果:

thenApply和handle的区别:
thenApply执行的时候,有异常的则整个执行链会中断,直接抛出异常。
handle有异常也可以往下一步走,根据带的异常参数可以进一步处理

thenAccept
接收前面任务的返回结果,当前节点处理,并不返回结果。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(\"step 1\");
return 10;
}).thenAccept(a->{
System.out.println(\"res \"+a);
});applyToEither
在多个任务段同时执行时,哪个任务段用时最少,就返回哪个
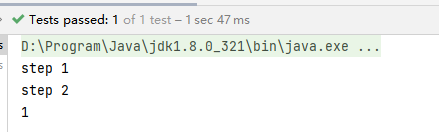
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(\"step 1\");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
}).applyToEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(\"step 2\");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 2;
}), a -> {
return a;
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());执行结果:
thenCombine
合并多个任务段的返回结果
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(\"step 1\");
return IntStream.range(1, 11).sum();
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(\"step 2\");
return IntStream.range(11, 21).sum();
}), (a, b) -> a + b)
.thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(\"step 3\");
return IntStream.range(21, 31).sum();
}), (a, b) -> a + b);
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/hitechr/p/16423413.html
本站部分图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园