Restful
1.REST架构的主要原则
1.1 对网络上所有的资源都有一个资源标志符
1.2 对资源的操作不会改变标识符
1.3 同一资源有多种表现形式(xml、json)、
1.4 所有操作都是无状态的(Stateless)
符合上述REST原则的架构方式称为Restful
2.URI和URL区别
URI:http://example.com/users/
URL:http://example.com/users/{user} (one for each user)
2.1.什么是无状态性
使得客户端和服务器端不必保存对方的详细信息,服务器只需要处理当前的请求,不需了解请求的历史。可以更容易的释放资源,让服务器利用Pool(连接池)技术来提高稳定性和性能。
3.Restful操作
RESTful是一种常见的REST应用,是遵循REST风格的web服务,REST式的web服务是一种ROA(面向资源的架构)。更加安全!!
| http方法 | 资源操作 | 幂等 | 安全 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | SELECT | 是 | 是 |
| POST | INSERT | 否 | 否 |
| PUT | UPDATE | 是 | 否 |
| DELETE | DELETE | 是 | 否 |
注:幂等性:对同一REST接口的多次访问,得到的资源状态是相同的。
安全性:对该REST接口访问,不会使服务器端资源的状态发生改变。
3.1接口示例
传统URL请求格式:
http:/127.0.0.1/test/query/2 http:/127.0.0.1/test/query?id=1 GET 根据用户id查询用户数据
http:/127.0.0.1/test/save POST 新增用户
http:/127.0.0.1/test/update POST 修改用户信息
http:/127.0.0.1/test/delete GET/POST 删除用户信息
RESTful请求格式:
http:/127.0.0.1/test/1 GET 根据用户id查询用户数据
http:/127.0.0.1/test POST 新增用户
http:/127.0.0.1/test PUT 修改用户信息
http:/127.0.0.1/test/1 DELETE 删除用户信息
4.Http状态码
4.1一般情况:
200:请求响应成功 200
3xx:请求重定向 重定向:你重新到我给你新位置去;
4xx:找不到资源 404 资源不存在;
5xx:服务器代码错误 500 502:网关错误
4.2具体情况:
HttpStatus = {
//Informational 1xx 信息
\'100\' : \'Continue\', //继续
\'101\' : \'Switching Protocols\', //交换协议
//Successful 2xx 成功
\'200\' : \'OK\', //OK
\'201\' : \'Created\', //创建
\'202\' : \'Accepted\', //已接受
\'203\' : \'Non-Authoritative Information\', //非权威信息
\'204\' : \'No Content\', //成功,但没有内容
\'205\' : \'Reset Content\', //重置内容
\'206\' : \'Partial Content\', //部分内容
//Redirection 3xx 重定向
\'300\' : \'Multiple Choices\', //多种选择
\'301\' : \'Moved Permanently\', //永久移动
\'302\' : \'Found\', //找到
\'303\' : \'See Other\', //参见其他
\'304\' : \'Not Modified\', //未修改
\'305\' : \'Use Proxy\', //使用代理
\'306\' : \'Unused\', //未使用
\'307\' : \'Temporary Redirect\', //暂时重定向
//Client Error 4xx 客户端错误
\'400\' : \'Bad Request\', //错误的请求
\'401\' : \'Unauthorized\', //未经授权
\'402\' : \'Payment Required\', //付费请求
\'403\' : \'Forbidden\', //禁止
\'404\' : \'Not Found\', //没有找到
\'405\' : \'Method Not Allowed\', //方法不允许
\'406\' : \'Not Acceptable\', //不可接受
\'407\' : \'Proxy Authentication Required\', //需要代理身份验证
\'408\' : \'Request Timeout\', //请求超时
\'409\' : \'Conflict\', //指令冲突
\'410\' : \'Gone\', //文档永久地离开了指定的位置
\'411\' : \'Length Required\', //需要Content-Length头请求
\'412\' : \'Precondition Failed\', //前提条件失败
\'413\' : \'Request Entity Too Large\', //请求实体太大
\'414\' : \'Request-URI Too Long\', //请求URI太长
\'415\' : \'Unsupported Media Type\', //不支持的媒体类型
\'416\' : \'Requested Range Not Satisfiable\', //请求的范围不可满足
\'417\' : \'Expectation Failed\', //期望失败
//Server Error 5xx 服务器错误
\'500\' : \'Internal Server Error\', //内部服务器错误
\'501\' : \'Not Implemented\', //未实现
\'502\' : \'Bad Gateway\', //错误的网关
\'503\' : \'Service Unavailable\', //服务不可用
\'504\' : \'Gateway Timeout\', //网关超时
\'505\' : \'HTTP Version Not Supported\' //HTTP版本不支持
};
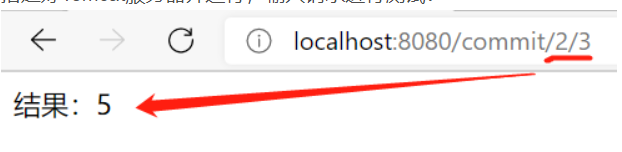
5.测试
@Controller
public class RestFulController {
//映射访问路径
@RequestMapping(\"/commit/{p1}/{p2}\")
//在SpringMVC中可以使用 @PathVariable,让方法参数的值对应绑定到一个URI变量上
public ModelAndView index(@PathVariable int p1, @PathVariable int p2, ModelAndView mv){
int result = p1 + p2;
//实例化一个ModelAndView对象用于向视图中传值
mv.addObject(\"msg\",\"结果:\" + result);
//返回视图
mv.setViewName(\"test\");
return mv;
}
}
也可以使用method属性指定类型
@RequestMapping(value = \"/hello\",method = {RequestMethod.POST})
public String index2(Model model){
model.addAttribute(\"msg\", \"hello!\");
return \"test\";
}
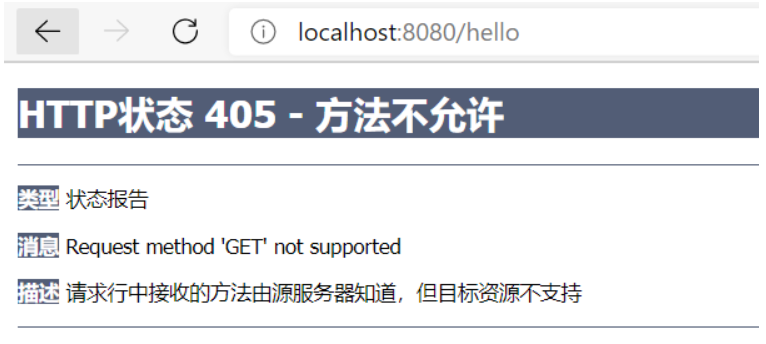
但浏览器地址栏进行访问是通过GET方式进行的 ,我们定义的是POST方法-所以报错不匹配
改为GET
@RequestMapping(value = \"/hello\",method = {RequestMethod.GET})
//我们一般采用这种方式:@GetMapping(\"/hello\")
public String index2(Model model){
model.addAttribute(\"msg\", \"hello!\");
return \"test\";
}
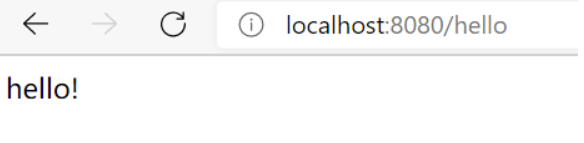
我们可以看到Method 方式太长,不方便,我们可以用延伸的方法
@GetMapping:扮演的是@RequestMapping(method =RequestMethod.GET) 的快捷方式。
@PostMapping (method =RequestMethod.GET)
@PutMapping (method =RequestMethod.POST)
@DeleteMapping (method =RequestMethod.DELETE)
@PatchMapping (method =RequestMethod.PATCH)
如:
如果是地址栏输入(GET)可以调用 index方法:
@GetMapping(\"/commit/{p1}/{p2}\")
//在SpringMVC中可以使用 @PathVariable,让方法参数的值对应绑定到一个URI变量上
public ModelAndView index(@PathVariable int p1, @PathVariable int p2, ModelAndView mv){
int result = p1 + p2;
//实例化一个ModelAndView对象用于向视图中传值
mv.addObject(\"msg\",\"结果1:\" + result);
//返回视图
mv.setViewName(\"test\");
return mv;
}
如果前端页面form表单 method为POST,则调用index2方法
@PostMapping(\"/commit/{p1}/{p2}\")
//在SpringMVC中可以使用 @PathVariable,让方法参数的值对应绑定到一个URI变量上
public ModelAndView index2(@PathVariable int p1, @PathVariable int p2, ModelAndView mv){
int result = p1 + p2;
//实例化一个ModelAndView对象用于向视图中传值
mv.addObject(\"msg\",\"结果2:\" + result);
//返回视图
mv.setViewName(\"test\");
return mv;
}
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/JayZzzWh/p/16602501.html
本站部分图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园