Java集合06
13.Map接口02
13.2Map接口常用方法
- put():添加
- remove():根据键键删除映射关系
- get():根据键获取值
- size():获取元素个数
- isEnpty():判断个数是否为0
- clear():清除
- containsKey():查找键是否存在
例子1:Map接口常用方法
package li.map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@SuppressWarnings(\"all\")
public class MapMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
// 1.put():添加
map.put(\"罗贯中\",new Book(\"111\",99));//ok
map.put(\"罗贯中\",\"三国演义\");//替换上一个value
map.put(\"施耐庵\",\"666\");//ok
map.put(\"克鲁苏\",\"666\");//ok
map.put(null,\"空空如也\");//ok
map.put(\"空空如也\",null);//ok
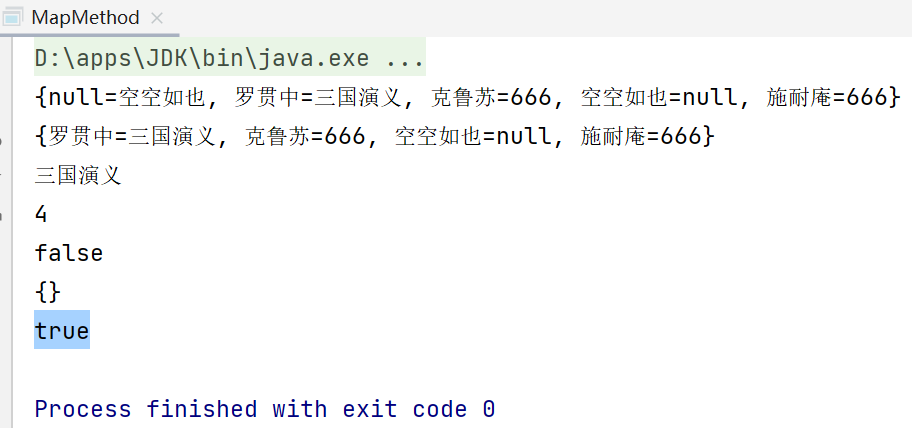
System.out.println(map);
// 2.remove():根据键键删除映射关系
map.remove(null);
System.out.println(map);//null对应的\"空空如也\"没有了
// 3. get():根据键获取值,返回一个Object类型
System.out.println(map.get(\"罗贯中\"));//三国演义
// 4. size():获取k-v对数
System.out.println(map.size());//4
// 5. isEnpty():判断个数是否为0
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());//false
// 6. clear():将所有k-v清空
map.clear();
System.out.println(map);//{}
// 7. containsKey():查找键是否存在
map.put(\"我是123\",\"我是123的value\");
System.out.println(map.containsKey(\"我是123\"));//true
}
}
class Book{
private String name;
private int price;
public Book(String name, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return \"Book{\" +
\"name=\'\" + name + \'\\\'\' +
\", price=\" + price +
\'}\';
}
}
13.3Map接口六大遍历方式

- containsKey:查找键是否存在
- keySet:获取所有的键
- entrySet:获取所有的关系k-v
- values:获取所有的值
例子:
package li.map;
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings(\"all\")
public class MapFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(\"罗贯中\", new Book(\"111\", 99));
map.put(\"罗贯中\", \"三国演义\");
map.put(\"施耐庵\", \"666\");
map.put(\"克鲁苏\", \"666\");
map.put(null, \"空空如也\");
map.put(\"空空如也\", null);
//第一组:先取出所有的key,通过key取出对应的value
Set keySet = map.keySet();
System.out.println(\"----增强for----\");
//增强for
for (Object key : keySet) {
System.out.println(key + \"-\" + map.get(key));//get():根据键获取值
}
System.out.println(\"----迭代器----\");
//迭代器
Iterator iterator = keySet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object key = iterator.next();
System.out.println(key + \"-\" + map.get(key));
}
//第二组:把所有的values值取出
Collection values = map.values();
//这里可以使用所有collection使用的遍历方法
//增强for:
System.out.println(\"---取出所有的value 增强for---\");
for (Object value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
//迭代器:
System.out.println(\"---取出所有的value 迭代器:---\");
Iterator iterator2 = values.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
Object value = iterator2.next();
System.out.println(value);
}
//第三组:通过EntrySet直接取出k-v对
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();//EntrySet<Map.Entry<K,V>>
//(1)增强for
System.out.println(\"---使用EntrySet的增强for---\");
for (Object entry : entrySet) {
//将entry转成 Map.Entry
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey()+\"-\"+m.getValue());
}
//(2)迭代器:
System.out.println(\"---使用EntrySet的迭代器---\");
Iterator iterator3 = entrySet.iterator();
while (iterator3.hasNext()) {
Object entry = iterator3.next();//这里next取出来的类型本质上是Node,让偶向上转型为Object
//System.out.println(next.getClass());//class java.util.HashMap$Node
//向下转型Object---> Map.Entry
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry)entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey()+\"-\"+m.getValue());
}
}
}
13.4Map课堂练习
使用HashMap添加三个员工对象,要求:
键:员工id
值:员工对象
并遍历显示工资>18000的员工(遍历方式最少两种)
员工类:姓名、工资、员工id
练习:
package li.map;
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings(\"all\")
public class MapExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(1, new Employee(\"smith\", 8800, 1));
map.put(2, new Employee(\"John\", 18900, 2));
map.put(3, new Employee(\"Jack\", 8900, 3));
map.put(4, new Employee(\"Marry\", 19900, 4));
map.put(5, new Employee(\"Jack\", 3000, 5));
//keySet
Set keySet = map.keySet();
System.out.println(\"---keySet的增强for---\");
for (Object key : keySet) {
Employee value = (Employee) map.get(key);//将获得的value对象向下转型为Employee类型
double salary = value.getSalary();//获取工资
if (salary > 18000) {
System.out.println(map.get(key));
}//判断输出
}
System.out.println(\"---keySet的迭代器---\");
Iterator iterator = keySet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object key = iterator.next();
Employee value = (Employee) map.get(key);//将获得的value对象向下转型为Employee类型
double salary = value.getSalary();//获取工资
if (salary > 18000) {
System.out.println(map.get(key));
}//判断输出
}
//EntrySet
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
System.out.println(\"---entrySet的增强for---\");
for (Object entry : entrySet) {//entry代表一对k-v
//将entry向下转型转成 Map.Entry
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) entry;
Employee employee = (Employee) m.getValue();
double salary = employee.getSalary();
if (salary > 18000) {//判断输出
System.out.println(m.getValue());
}
}
System.out.println(\"---entrySet的迭代器---\");
Iterator iterator2 = entrySet.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
Object entry = iterator2.next();
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) entry;//将Object强转为Map.Entry类型
Employee employee = (Employee) m.getValue();
double salary = employee.getSalary();
if (salary > 18000) {//判断输出
System.out.println(m.getValue());
}
}
}
}
class Employee {
private String name;
private double salary;
private int id;
public Employee(String name, double salary, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return \"Employee{\" +
\"name=\'\" + name + \'\\\'\' +
\", salary=\" + salary +
\", id=\" + id +
\'}\';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
13.5HashMap小结
- Map接口的常用实现类:HashMap、Hashtable、Properties
- HashMap是Map接口使用频率最高的实现类
- HashMap是以key-value对的方式来存储数据(HashMap$Node类型)
- key不能重复,value可以重复。允许使用null键和null值
- 如果添加相同的key键,则会覆盖原来的key-value,等同于修改(key不会替换,value会替换)
- 与HashSet一样,不保证映射的顺序,因为底层是以hash表的顺序来存储的。(JDK8的HashMap底层:数组+链表+红黑树)
- HashMap没有实现同步,因此线程不安全,方法没有做同步互斥的操作,没有synchronized
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/liyuelian/p/16608467.html
本站部分图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园