在日常的开发工作中,为了保证落库数据的完整性,参数校验绝对是必不可少的一部分,本篇文章就来讲解下在项目中该如何优雅的校验参数。
假设有一个新增学员的接口,一般第一步我们都会先校验学员信息是否正确,然后才会落库,简单起见,假设新增学员时只有2个字段:姓名、年龄。
@Data
public class StudentVO {
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 年龄
*/
private Integer age;
}
要求为:姓名和年龄必填,姓名不能超过20个字符。
1. 最原始的写法
先来看下最原始的写法,相信大多数人都这么写过,或者说在初学Java时都这么写过:
public String validateStudentVO(StudentVO studentVO) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(studentVO.getName())) {
return \"姓名不能为空\";
}
if (studentVO.getName().length() > 20) {
return \"姓名不能超过20个字符\";
}
if (studentVO.getAge() == null) {
return \"年龄不能为空\";
}
return null;
}
这么写最好理解,但一般一个项目中都会有很多接口,如果都这么写的话,重复代码会非常多,显得非常臃肿,而且对于一个工作多年的开发来说,如果每天都写这样的代码,会觉得特别没有技术含量。
2. Bean Validation
既然有需求场景,就会有规范,这个规范就是Bean Validation,官网地址是 https://beanvalidation.org/。
Bean Validation先后经历了1.0(JSR 303)、1.1(JSR 349)、2.0(JSR 380)这3个版本,目前项目中使用比较多的是Bean Validation 2.0,本篇文章讲解的内容也是基于Bean Validation 2.0版本。
Bean Validation 2.0之后,现在改名叫Jakarta Bean Validation了。
pom依赖坐标如下所示:
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.validation</groupId>
<artifactId>validation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.Final</version>
</dependency>
不过从2.0.1.Final之后的版本依赖都改为了jakarta.validation-api:

新版本pom依赖坐标如下所示:
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.validation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.validation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2</version>
</dependency>
3. Hibernate Validator
Hibernate Validator是 Bean Validation 的参考实现 ,不仅提供了规范中所有内置constraint的实现,除此之外还提供了一些附加的 constraint。
pom依赖坐标如下所示:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.2.5.Final</version>
</dependency>
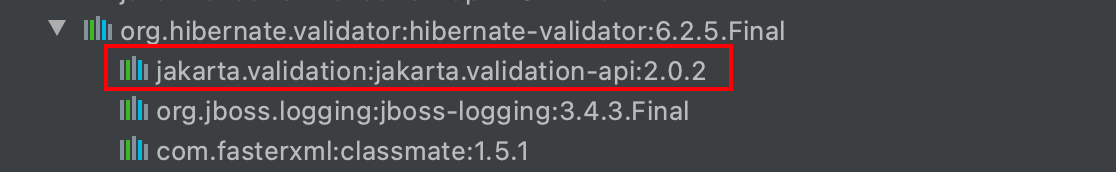
因为hibernate-validator中已经包含了validation-api,因此项目中如果引入了hibernate-validator,就没必要重复引入validation-api了:
4. Bean Validation 2.0原生注解
Bean Validation 2.0中包含了22个注解,如下图所示:

接下来详细讲解下这22个注解的用途。
4.1 @AssertTrue
作用:被标记的元素必须为true。
支持的Java类型:boolean、Boolean。
使用示例:
@AssertTrue
private Boolean newStudent;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setNewStudent(false);
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
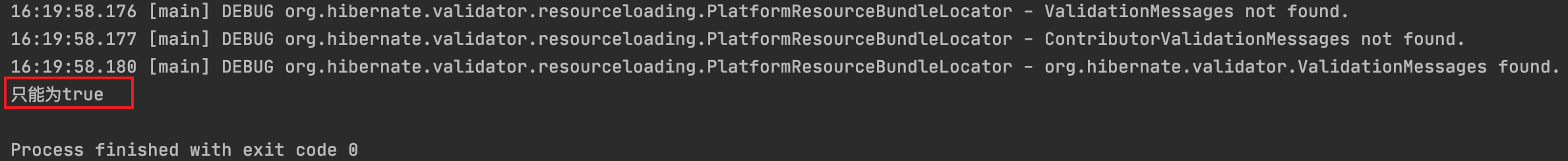
输出结果:
上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@AssertTrue(message = \"newStudent必须为true\")
private Boolean newStudent;
效果如下图所示:

注意事项:
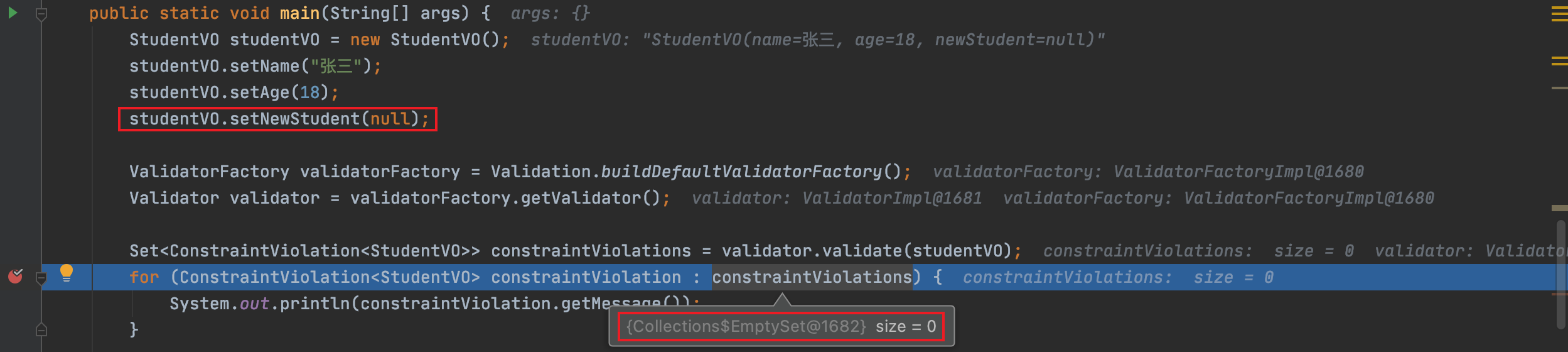
1)@AssertTrue注解识别不了字段值为null的场景:
2)如果将@AssertTrue注解使用在boolean、Boolean之外的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常:
@AssertTrue
private String name;

4.2 @AssertFalse
作用:被标记的元素值必须为false。
其余的和@AssertTrue注解一致。
使用示例:
@AssertFalse(message = \"newStudent必须为false\")
private Boolean newStudent;
4.3 @DecimalMax
作用:被标记的元素必须小于或等于指定的值。
支持的Java类型:BigDecimal、BigInteger、byte、Byte、short、Short、int、Integer、long、Long、String。
使用示例:
@DecimalMax(value = \"30000\")
private BigDecimal balance;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setBalance(new BigDecimal(\"30001\"));
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@DecimalMax(value = \"30000\", message = \"账户余额必须小于或等于30000\")
private BigDecimal balance;
效果如下图所示:

注意事项:
1)@DecimalMax注解识别不了字段值为null的场景:

2)如果将@DecimalMax注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常:
@DecimalMax(value = \"30000\", message = \"账户余额必须小于或等于30000\")
private Boolean newStudent;

4.4 @DecimalMin
作用:被标记的元素值必须大于或等于指定的值。
其余的和@DecimalMax注解一致。
使用示例:
@DecimalMin(value = \"5000\", message = \"充值余额必须大于或等于5000\")
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
4.5 @Digits
作用:被标记的元素整数位数和小数位数必须小于或等于指定的值。
支持的Java类型:BigDecimal、BigInteger、byte、Byte、short、Short、int、Integer、long、Long、String。
使用示例:
@Digits(integer = 6, fraction = 2)
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setRechargeAmount(new BigDecimal(\"100000.999\"));
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Digits(integer = 6, fraction = 2, message = \"充值金额只允许6位整数、2位小数\")
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
效果如下图所示:

注意事项:
1)@Digits注解识别不了字段值为null的场景:

2)如果将@Digits注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常:
@Digits(integer = 6, fraction = 2, message = \"充值金额只允许6位整数、2位小数\")
private Boolean newStudent;

4.6 @Email
作用:被标记的元素必须是邮箱地址。
支持的Java类型:String。
使用示例:
@Email
private String email;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setEmail(\"活着\");
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
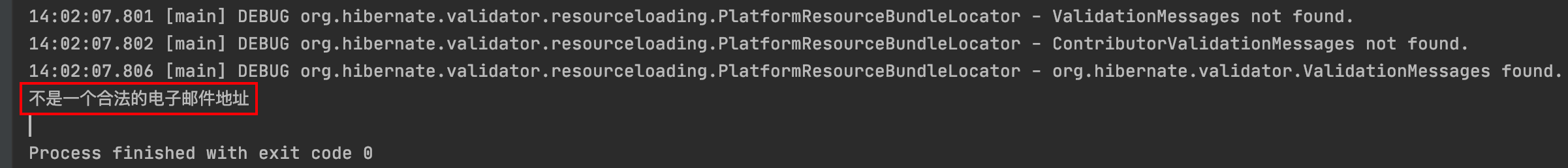
输出结果:
上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Email(message = \"无效的电子邮件地址\")
private String email;
效果如下图所示:

注意事项:
1)@Email注解识别不了字段值为null或空字符串\"\"的场景:
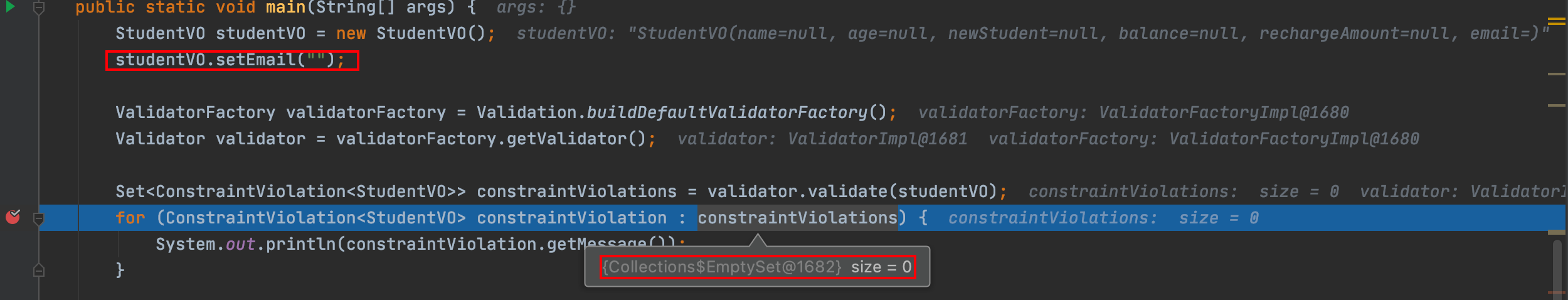
2)如果将@Email注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4.7 @Future
作用:被标记的元素必须为当前时间之后。
支持的Java类型:Date、Calendar、Instant、LocalDate、LocalDateTime、LocalTime等。
使用示例:
@Future
private Date startingDate;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setStartingDate(new Date());
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:
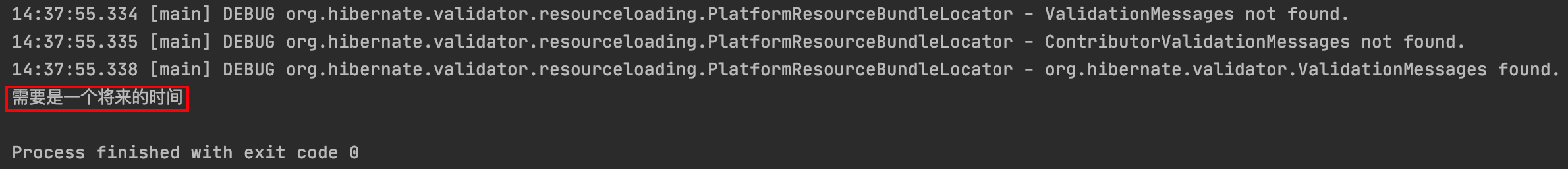
注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Future(message = \"必须是一个将来的时间\")
private Date startingDate;
2)@Future注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@Future注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4.8 @FutureOrPresent
作用:被标记的元素必须为当前时间或之后。
支持的Java类型:Date、Calendar、Instant、LocalDate、LocalDateTime、LocalTime等。
使用示例:
@FutureOrPresent
private Date startingDate;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setStartingDate(DateUtils.addMilliseconds(new Date(), 1));
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:
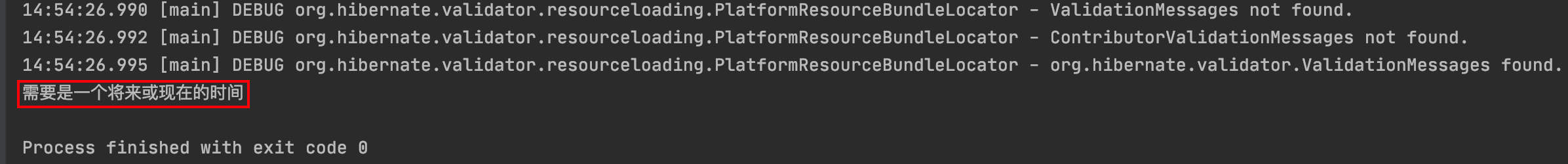
注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@FutureOrPresent(message = \"必须是一个将来或现在的时间\")
private Date startingDate;
2)@FutureOrPresent注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@FutureOrPresent注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4.9 @Past
作用:被标记的元素必须为当前时间之前。
支持的Java类型:Date、Calendar、Instant、LocalDate、LocalDateTime、LocalTime等。
使用示例:
@Past
private Date latestAttendanceTime;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setLatestAttendanceTime(DateUtils.addMinutes(new Date(), 10));
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Past(message = \"必须是一个过去的时间\")
private Date latestAttendanceTime;
2)@Past注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@Past注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4.10 @PastOrPresent
作用:被标记的元素必须为当前时间或之前。
支持的Java类型:Date、Calendar、Instant、LocalDate、LocalDateTime、LocalTime等。
使用示例:
@PastOrPresent
private Date latestAttendanceTime;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setLatestAttendanceTime(DateUtils.addMinutes(new Date(), 10));
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@PastOrPresent(message = \"必须是一个过去或现在的时间\")
private Date latestAttendanceTime;
2)@PastOrPresent注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@PastOrPresent注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4.11 @Max
作用:被标记的元素必须小于或等于指定的值。
支持的Java类型:BigDecimal、BigInteger、byte、Byte、short、Short、int、Integer、long、Long、String。
使用示例:
@Max(value = 10000)
private BigDecimal balance;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setBalance(new BigDecimal(\"10000.01\"));
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Max(value = 10000, message = \"必须小于或等于10000\")
private BigDecimal balance;
2)@Max注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@Max注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4.12 @Min
作用:被标记的元素必须大于或等于指定的值。
支持的Java类型:BigDecimal、BigInteger、byte、Byte、short、Short、int、Integer、long、Long、String。
使用示例:
@Min(value = 5000)
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setRechargeAmount(new BigDecimal(\"4999\"));
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Min(value = 5000, message = \"必须大于或等于5000\")
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
2)@Min注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@Min注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4.13 @Negative
作用:被标记的元素必须是负数。
支持的Java类型:BigDecimal、BigInteger、byte、Byte、short、Short、int、Integer、long、Long、float、Float、
double、Double。
使用示例:
@Negative
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setRechargeAmount(new BigDecimal(\"0\"));
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Negative(message = \"金额必须是负数\")
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
2)@Negative注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@Negative注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4.14 @NegativeOrZero
@NegativeOrZero注解和@Negative注解基本一致,唯一的区别是被标记的元素除了可以是负数,也可以是零。
使用示例:
@NegativeOrZero(message = \"金额必须是负数或零\")
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
4.15 @Positive
作用:被标记的元素必须是正数。
支持的Java类型:BigDecimal、BigInteger、byte、Byte、short、Short、int、Integer、long、Long、float、Float、
double、Double。
使用示例:
@Positive
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setRechargeAmount(new BigDecimal(\"0\"));
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Positive(message = \"充值金额必须是正数\")
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
2)@Positive注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@Positive注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4.16 @PositiveOrZero
@PositiveOrZero注解和@Positive注解基本一致,唯一的区别是被标记的元素除了可以是正数,也可以是零。
使用示例:
@PositiveOrZero(message = \"充值金额必须是正数或零\")
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
4.17 @Null
作用:被标记的元素必须为null。
支持的Java类型:Object。
使用示例:
@Null
private String namePinYin;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setNamePinYin(\"zhangsan\");
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Null(message = \"姓名拼音必须为null\")
private String namePinYin;
4.18 @NotNull
作用:被标记的元素必须不为null。
其余和@Null注解一致。
4.19 @NotEmpty
作用:被标记的元素不为null,且不为空(字符串的话,就是length要大于0,集合的话,就是size要大于0)。
支持的Java类型:String、Collection、Map、Array。
使用示例:
/**
* 姓名
*/
@NotEmpty
private String name;
/**
* 家长信息
*/
@NotEmpty
private List<ParentVO> parentVOList;
ParentVO如下所示:
@Data
public class ParentVO {
/**
* 姓名
*/
@NotEmpty(message = \"姓名不能为空\")
private String name;
/**
* 手机号
*/
@NotEmpty(message = \"手机号不能为空\")
private String mobile;
}
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setName(\"\");
studentVO.setParentVOList(new ArrayList<>());
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@NotEmpty(message = \"姓名不能为空\")
private String name;
2)如果将@NotEmpty注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
3)嵌套验证问题
简单修改下上面的验证代码:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setName(\"张三\");
ParentVO parentVO = new ParentVO();
studentVO.setParentVOList(Lists.newArrayList(parentVO));
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
此时的输出结果如下所示:

从输出结果可以看出,StudentVO里增加的@NotEmpty注解生效了,但嵌套的ParentVO里的校验注解并未生效,如果想生效的话,需要加上@Valid注解:
/**
* 家长信息
*/
@Valid
@NotEmpty
private List<ParentVO> parentVOList;
再次执行上面的验证代码,输出结果如下图所示:

可以看出,嵌套的ParentVO里的校验注解也生效了。
4.20 @NotBlank
作用:被标记的元素不为null,且必须有一个非空格字符。
这里提下和
@NotEmpty的区别,作用于字符串的话,@NotEmpty能校验出null、”“这2种场景,而
@NotBlank能校验出null、”“、” “这3种场景,作用于集合的话,
@NotEmpty支持,但@NotBlank不支持。
支持的Java类型:String。
使用示例:
@NotBlank
private String name;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setName(\" \");
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@NotBlank(message = \"姓名不能为空\")
private String name;
2)如果将@NotBlank注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4.21 @Size
作用:被标记的元素长度/大小必须在指定的范围内(字符串的话,就是length要在指定的范围内,集合的话,就是size要在指定的范围内)。
支持的Java类型:String、Collection、Map、Array。
使用示例:
@Size(min = 2, max = 5)
private String name;
@Size(min = 1, max = 5)
private List<ParentVO> parentVOList;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setName(\"张三李四王五\");
studentVO.setParentVOList(new ArrayList<>());
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Size(min = 2, max = 5, message = \"姓名不能少于2个字符,不能多于5个字符\")
private String name;
@Size(min = 1, max = 5, message = \"至少添加一位家长信息,最多不能超过5位\")
private List<ParentVO> parentVOList;
2)@Size注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
2)如果将@Size注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4.22 @Pattern
作用:被标记的元素必须匹配指定的正则表达式。
支持的Java类型:String。
使用示例:
@Pattern(regexp = \"^[1-9]\\\\d{5}$\")
private String postcode;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setPostcode(\"2000001\");
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Pattern(regexp = \"^[1-9]\\\\d{5}$\", message = \"邮政编码格式错误\")
private String postcode;
2)@Pattern注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@Pattern注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
5. Hibernate Validator扩展注解
Hibernate Validator除了支持上面提到的22个原生注解外,还扩展了一些注解:

接下来详细讲解几个常用的。
5.1 @Length
作用:被标记的元素必须在指定的长度范围内。
支持的Java类型:String。
使用示例:
@Length(min = 2, max = 5)
private String name;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setName(\"张三李四王五\");
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Length(min = 2, max = 5, message = \"姓名不能少于2个字符,不能多于5个字符\")
private String name;
2)@Length注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@Length注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
5.2 @Range
@Range注解相当于同时融合了@Min注解和@Max注解的功能,如下图所示:

因此它的作用是:被注解的元素必须大于或等于指定的最小值,小于或等于指定的最大值。
它支持的Java类型也和@Min注解和@Max注解一致:
BigDecimal、BigInteger、byte、Byte、short、Short、int、Integer、long、Long、String。
使用示例:
@Range(min = 1000L, max = 10000L)
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setRechargeAmount(new BigDecimal(\"500\"));
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@Range(min = 1000L, max = 10000L, message = \"至少充值1000,最多充值10000\")
private BigDecimal rechargeAmount;
2)@Range注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@Range注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
4)不建议将@Range注解使用在String类型上。
5.3 @URL
作用:被标记的元素必须是一个有效的url地址。
它的内部其实是使用了@Pattern注解,如下图所示:

因此它支持的Java类型和@Pattern注解一致:String。
使用示例:
@URL
private String url;
验证:
StudentVO studentVO = new StudentVO();
studentVO.setRechargeAmount(new BigDecimal(\"1000\"));
studentVO.setUrl(\"url地址\");
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<StudentVO>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(studentVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<StudentVO> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
输出结果:

注意事项:
1)上面输出的message是默认的,在实际使用时可以自定义:
@URL(message = \"无效的url地址\")
private String url;
2)@URL注解识别不了字段值为null的场景。
3)如果将@URL注解使用在不支持的Java类型,程序会抛出javax.validation.UnexpectedTypeException异常。
6. Spring Web项目
如果项目本身是基于Spring Web的,可以使用@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler来全局处理参数校验。
首先,新建一个全局异常处理器,并添加@RestControllerAdvice注解:
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
}
说明:因为接口返回的是json,这里使用
@RestControllerAdvice等价于同时使用了@ControllerAdvice和@ResponseBody。
接着,我们将文初的StudentVO修改为:
import lombok.Data;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Length;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
@Data
public class StudentVO {
/**
* 姓名
*/
@NotBlank(message = \"姓名不能为空\")
@Length(max = 20, message = \"姓名不能超过20个字符\")
private String name;
/**
* 年龄
*/
@NotNull(message = \"年龄不能为空\")
private Integer age;
}
然后在api接口的参数前增加@Valid注解:
@RestController
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@PostMapping(\"student/add\")
public CommonResponse<Void> add(@RequestBody @Valid StudentVO studentVO) {
studentService.add(studentVO);
return CommonResponse.success();
}
}
6.1 处理MethodArgumentNotValidException异常
在全局异常处理器中添加MethodArgumentNotValidException异常处理逻辑:
/**
* 处理MethodArgumentNotValidException
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
log.error(\"方法参数不正确\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(),
\"参数错误:\" + e.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().get(0).getDefaultMessage());
}
最后使用postman调用接口进行验证,如下图所示:

从接口返回结果,可以看出,全局异常处理器成功的处理了MethodArgumentNotValidException异常的逻辑,因为上面调用接口,其实程序是抛出了org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException异常,不过因为在全局异常处理器中定义了该异常的处理逻辑,所以程序按照定义的格式返回给了前端,而不是直接将异常抛给前端:

6.2 处理HttpMessageNotReadableException异常
上面的接口,如果我们不传参数,程序会抛出org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotReadableException异常,如下图所示:

因此需要在全局异常处理器中添加HttpMessageNotReadableException异常处理逻辑:
/**
* 处理HttpMessageNotReadableException
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(HttpMessageNotReadableException.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleHttpMessageNotReadableException(HttpMessageNotReadableException e) {
log.error(\"参数错误\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), \"参数错误\");
}
使用postman调用接口进行验证,如下图所示:

6.3 处理MissingServletRequestParameterException异常
假设我们有一个根据名字查询学员的GET请求的接口:
@GetMapping(\"student/get\")
public CommonResponse<StudentVO> get(@RequestParam String name) {
StudentVO studentVO = studentService.getByName(name);
return CommonResponse.success(studentVO);
}
但调用时,我们不传递参数name,程序会抛出org.springframework.web.bind.MissingServletRequestParameterException异常,如下图所示:

因此需要在全局异常处理器中添加MissingServletRequestParameterException异常处理逻辑:
/**
* 处理MissingServletRequestParameterException
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(MissingServletRequestParameterException.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleMissingServletRequestParameterException(MissingServletRequestParameterException e) {
log.error(\"参数错误\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), \"参数错误\");
}
使用postman调用接口进行验证,如下图所示:

6.4 处理ConstraintViolationException异常
还是上面的查询学员接口,不仅要传参数name,还得保证参数name不能是个空字符串,因此需要在参数前加上@NotBlank注解:
@GetMapping(\"student/get\")
public CommonResponse<StudentVO> get(@RequestParam @NotBlank(message = \"名字不能为空\") String name) {
StudentVO studentVO = studentService.getByName(name);
return CommonResponse.success(studentVO);
}
并且需要在控制器Controller上添加@Validated注解:

注意事项:控制器上的
@Validated注解一定要添加,否则参数上加的@NotBlank注解不会生效。
此时调用接口,但参数name传递个空字符串,程序会抛出javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException异常,如下图所示:

因此需要在全局异常处理器中添加ConstraintViolationException异常处理逻辑:
/**
* 处理ConstraintViolationException
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleConstraintViolationException(ConstraintViolationException e) {
log.error(\"参数错误\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), e.getConstraintViolations().iterator().next().getMessage());
}
使用postman调用接口进行验证,如下图所示:

6.5 扩展
全局异常处理器除了处理上面提到的4个参数校验的异常,一般也会处理业务上抛出的异常,如Service层抛出的自定义异常:
@Service
public class StudentService {
public StudentVO getByName(String name) {
throw new ServiceException(\"学员不存在\");
}
}
/**
* 业务异常
*/
public class ServiceException extends RuntimeException {
public ServiceException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
所以一般全局异常处理器中都有处理ServiceException的逻辑:
/**
* 处理ServiceException
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(ServiceException.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleServiceException(ServiceException e) {
log.error(\"业务异常\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), e.getMessage());
}
因为异常有很多种类型,而本文中提到的只是其中的几个,因此为了起到兜底作用,可以在全局异常处理器中添加处理Exception异常的逻辑,当程序抛出未知的异常时,可以统一处理,返回某个固定的提示给前端:
/**
* 处理Exception
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleException(Exception e) {
log.error(\"系统异常\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), \"操作失败,请稍后重试\");
}
6.6 完整的GlobalExceptionHandler代码
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotReadableException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MissingServletRequestParameterException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException;
/**
* 全局异常处理器
*/
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**
* 处理MethodArgumentNotValidException
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
log.error(\"方法参数不正确\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(),
\"参数错误:\" + e.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().get(0).getDefaultMessage());
}
/**
* 处理HttpMessageNotReadableException
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(HttpMessageNotReadableException.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleHttpMessageNotReadableException(HttpMessageNotReadableException e) {
log.error(\"参数错误\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), \"参数错误\");
}
/**
* 处理MissingServletRequestParameterException
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(MissingServletRequestParameterException.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleMissingServletRequestParameterException(MissingServletRequestParameterException e) {
log.error(\"参数错误\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), \"参数错误\");
}
/**
* 处理ConstraintViolationException
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleConstraintViolationException(ConstraintViolationException e) {
log.error(\"参数错误\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), e.getConstraintViolations().iterator().next().getMessage());
}
/**
* 处理ServiceException
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(ServiceException.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleServiceException(ServiceException e) {
log.error(\"业务异常\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), e.getMessage());
}
/**
* 处理Exception
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public CommonResponse<Void> handleException(Exception e) {
log.error(\"系统异常\", e);
return CommonResponse.error(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), \"操作失败,请稍后重试\");
}
}
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/p/16997650.html
本站部分图文来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
 百木园
百木园